16 May 2025 to 8 January 2025
¶ Idea Tools for Participatory Intelligence · 16 May 2025 essay/tech
The personal computer was revolutionary because it was the first really general-purpose power-tool for ideas. Personal computers began as relatively primitive idea-tools, bulky and slow and isolated, but they have gotten small and fast and connected.
They have also, however, gotten less tool-like.
PCs used to start up with a blank screen and a single blinking cursor. Later, once spreadsheets were invented, 1-2-3 still opened with a blank screen and some row numbers. Later, once search engines were invented, Google still opened with a blank screen and a text box. These were all much more sophisticated tools than hammers, but they at least started with the same humility as the hammer, waiting quietly and patiently for your hand. We learned how to fill the blank screens, how to build.
Blank screens and patience have become rare. Our applications goad us restlessly with "recommendations", our web sites and search engines are interlaced with blaring ads, our appliances and applications are encrusted with presumptuous presets and supposedly special modes. The Popcorn button on your microwave and the Chill Vibes playlist in your music app are convenient if you want to make popcorn and then fall asleep before eating most of it, and individually clever and harmless, but in aggregate these things begin to reduce increasing fractions of your life to choosing among the manipulatively limited options offered by automated systems dedicated to their own purposes instead of yours.
And while the network effects and attention consumption of social media were already consolidating the control of these automated systems among a small number of large, domination-focused corporations, the Large Language Model era of AI threatens to hyper-accelerate this centralization and disempowerment. More and more of our individual lives, and of our collectively shared social existences, are constrained and manipulated by data and algorithms that we do not control or understand. And, worse, increasingly even the humans inside the corporations that control those algorithms don't actually know how they work. We are afflicted by systems to which we not only did not consent, but in fact could not give informed consent because their effects are not validated against human intentions, nor produced by explainable rules.
This is not the tools' fault. Idea tools can only express their makers' intentions and inattentions. If we want better idea tools that distribute explainable algorithmic power instead of consolidating mysterious control, we have to make them so that they operate that way. If we want tools that invite us to have and share and explore our own ideas, rather than obediently submitting whatever we are given, we have to think about each other as humans and inspirations, not subjects or users. If we want the astonishing potential of all this computation to be realized for humanity, rather than inflicted on it, we have to know what we want.
At Imbue we are trying to use computers and data and software and AI to help imagine and make better idea tools for participatory intelligence. Applications, ecosystems, protocols, languages, algorithms, policies, stories: these are all idea tools and we probably need all of them. This is a shared mission for humanity, not a VC plan for value-extraction. That's the point of participatory. The ideas that govern us, whether metaphorically in applications or literally in governments, should be explainable and understandable and accountable. The data on which automated judgments are based should be accessible so that those judgments can be validated and alternatives can be formulated and assessed. The problems that face us require all of our innumerable insights. The collective wisdom our combined individual intelligences produce belongs rightfully to us. We need tools that are predicated on our rights, dedicated to amplifying our creative capacity, and judged by how they help us improve our world. We need tools that not only reduce our isolation and passivity, but conduct our curious energy and help us recognize opportunities for discovery and joy.
This starts with us. Everything starts with us, all of us. There is no other way.
This belief is, itself, an idea tool: an impatient hammer we have made for ourselves.
Let's see what we can do with it.
They have also, however, gotten less tool-like.
PCs used to start up with a blank screen and a single blinking cursor. Later, once spreadsheets were invented, 1-2-3 still opened with a blank screen and some row numbers. Later, once search engines were invented, Google still opened with a blank screen and a text box. These were all much more sophisticated tools than hammers, but they at least started with the same humility as the hammer, waiting quietly and patiently for your hand. We learned how to fill the blank screens, how to build.
Blank screens and patience have become rare. Our applications goad us restlessly with "recommendations", our web sites and search engines are interlaced with blaring ads, our appliances and applications are encrusted with presumptuous presets and supposedly special modes. The Popcorn button on your microwave and the Chill Vibes playlist in your music app are convenient if you want to make popcorn and then fall asleep before eating most of it, and individually clever and harmless, but in aggregate these things begin to reduce increasing fractions of your life to choosing among the manipulatively limited options offered by automated systems dedicated to their own purposes instead of yours.
And while the network effects and attention consumption of social media were already consolidating the control of these automated systems among a small number of large, domination-focused corporations, the Large Language Model era of AI threatens to hyper-accelerate this centralization and disempowerment. More and more of our individual lives, and of our collectively shared social existences, are constrained and manipulated by data and algorithms that we do not control or understand. And, worse, increasingly even the humans inside the corporations that control those algorithms don't actually know how they work. We are afflicted by systems to which we not only did not consent, but in fact could not give informed consent because their effects are not validated against human intentions, nor produced by explainable rules.
This is not the tools' fault. Idea tools can only express their makers' intentions and inattentions. If we want better idea tools that distribute explainable algorithmic power instead of consolidating mysterious control, we have to make them so that they operate that way. If we want tools that invite us to have and share and explore our own ideas, rather than obediently submitting whatever we are given, we have to think about each other as humans and inspirations, not subjects or users. If we want the astonishing potential of all this computation to be realized for humanity, rather than inflicted on it, we have to know what we want.
At Imbue we are trying to use computers and data and software and AI to help imagine and make better idea tools for participatory intelligence. Applications, ecosystems, protocols, languages, algorithms, policies, stories: these are all idea tools and we probably need all of them. This is a shared mission for humanity, not a VC plan for value-extraction. That's the point of participatory. The ideas that govern us, whether metaphorically in applications or literally in governments, should be explainable and understandable and accountable. The data on which automated judgments are based should be accessible so that those judgments can be validated and alternatives can be formulated and assessed. The problems that face us require all of our innumerable insights. The collective wisdom our combined individual intelligences produce belongs rightfully to us. We need tools that are predicated on our rights, dedicated to amplifying our creative capacity, and judged by how they help us improve our world. We need tools that not only reduce our isolation and passivity, but conduct our curious energy and help us recognize opportunities for discovery and joy.
This starts with us. Everything starts with us, all of us. There is no other way.
This belief is, itself, an idea tool: an impatient hammer we have made for ourselves.
Let's see what we can do with it.
¶ Awkward and curious · 17 April 2025 listen/tech
Curio began as experiment in music-curiosity software, but is also increasingly an experiment in how to build personal software in general.
Personally, I organize my listening in weeks, and model those weeks in playlists. Curio has a page for looking at which artists you have put in your playlists, and how often. And because my playlists are dated, it makes sense to me to be able to filter mine by year. But because this may not make the same sense for your playlists, I didn't build a year-filtering feature, I built a filtering feature.
The controls for it are at the bottom of the Playlists page in Curio:

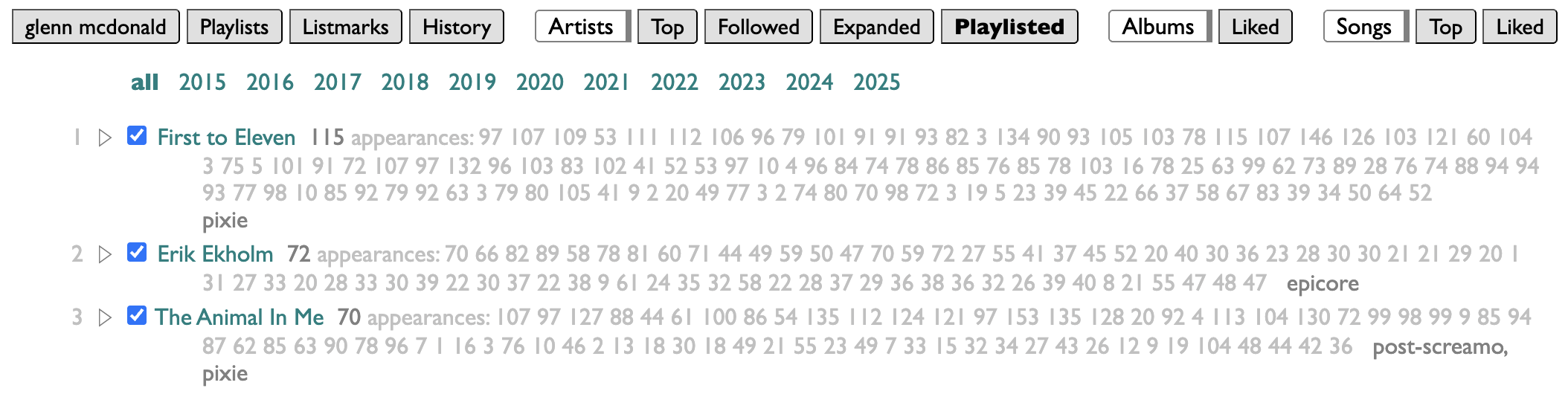
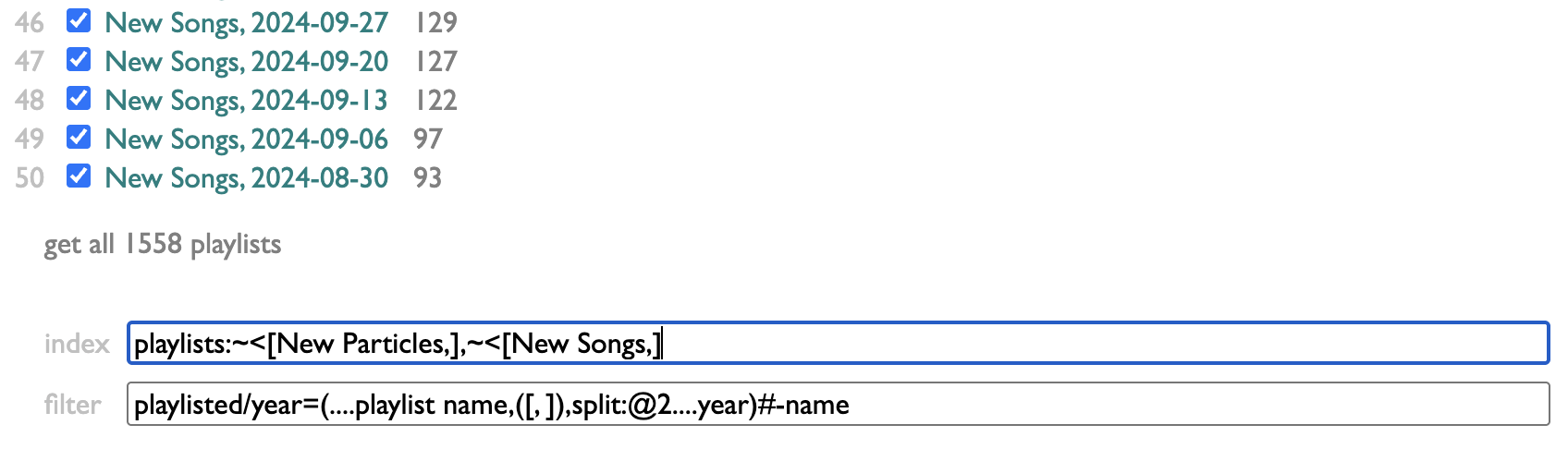
index lets you control which of your playlists are indexed. I make a lot of playlists that are not actually expressions of my own tastes or conduits of my listening, so I've chosen to only index the ones that begin with "New Particles," or "New Songs,". You can put any number of name-prefixes here, ending each one with an asterisk.
filter lets you provide a set of filters in the form of substrings to match against playlist titles. Separate them with commas, and if you start one of the filters with an asterisk, that will give you a magic filter that selects everything, labeled without the asterisk: so "*all" here produces an all-filter labeled "all".
That's kinda flexible, but having to type out the exact filters you want only makes sense if the set is small and doesn't change much, and only doing substring-matching against playlist names is a pretty limited scope.
So the other way you can configure filters is by writing a Dactal query. It has to start with playlisted, which gets you the list of all the tracks from all the indexed playlists.
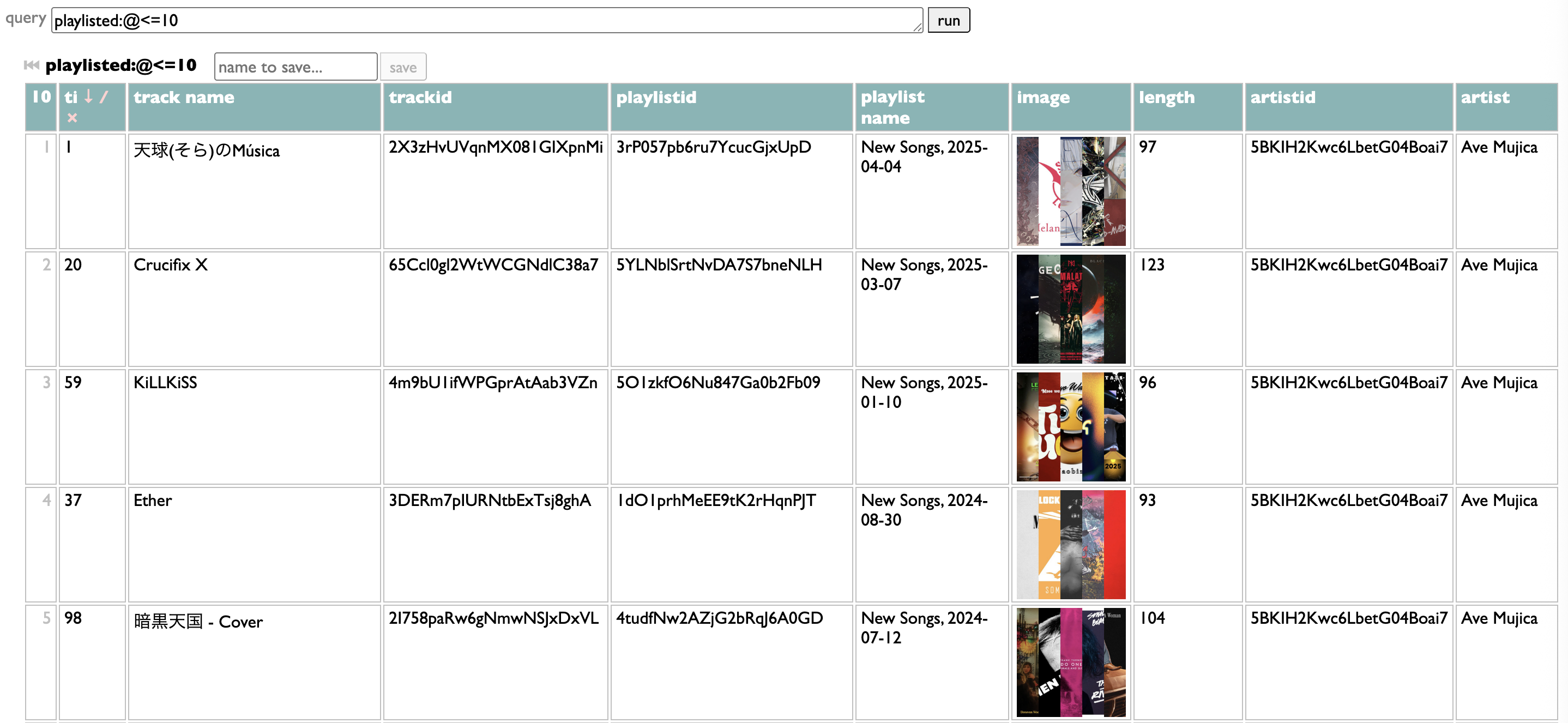
It has to end with groups of those tracks.
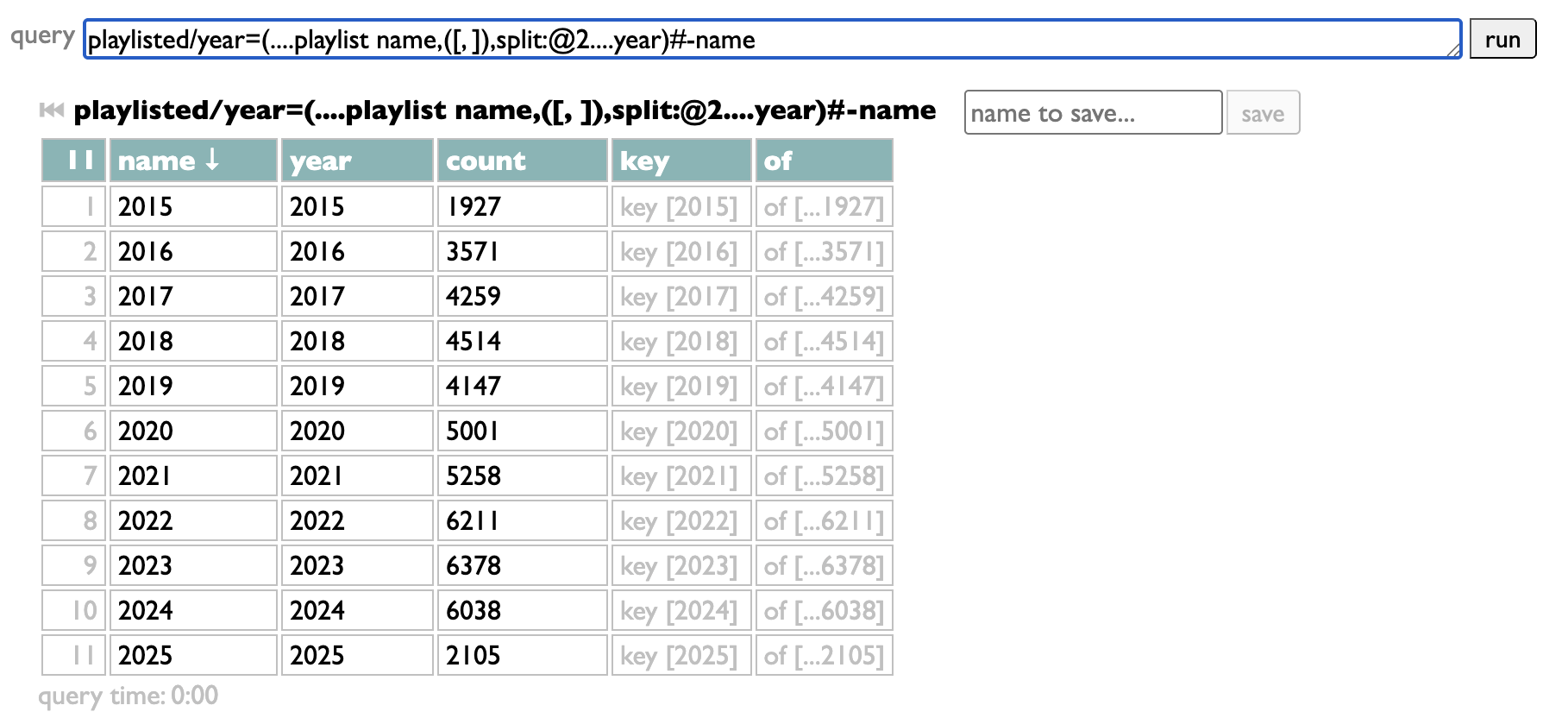
The groups are the filter choices. My query takes the playlist name, splits it at the comma to extract the date, pulls the year out of that date, groups by that year, and sorts the resulting year-groups in numeric order. But as long as your query starts with "playlisted" and ends with groups, in between it can do whatever you want. Once you have it working your way, just copy it into the "filter" box:

The magic "all" filter is added automatically if you're using a query. I should probably add an option to control that, but I haven't yet. This gets us back to:

...except dynamically, now, so I won't have to remember to add 2026 by hand, it will just appear when needed. Assuming, bravely, that neither AI nor fascists have consumed us before then.
If Curio were a commercial application, surely we would never ship a feature anywhere near this awkward and unguarded. But it isn't, and "we" is me, and I'm trying to imagine what the world could be like if your software invited you to be awkward and unguarded instead of pandered to; curious instead of customers.
PS: Also...
Personally, I organize my listening in weeks, and model those weeks in playlists. Curio has a page for looking at which artists you have put in your playlists, and how often. And because my playlists are dated, it makes sense to me to be able to filter mine by year. But because this may not make the same sense for your playlists, I didn't build a year-filtering feature, I built a filtering feature.
The controls for it are at the bottom of the Playlists page in Curio:

index lets you control which of your playlists are indexed. I make a lot of playlists that are not actually expressions of my own tastes or conduits of my listening, so I've chosen to only index the ones that begin with "New Particles," or "New Songs,". You can put any number of name-prefixes here, ending each one with an asterisk.
filter lets you provide a set of filters in the form of substrings to match against playlist titles. Separate them with commas, and if you start one of the filters with an asterisk, that will give you a magic filter that selects everything, labeled without the asterisk: so "*all" here produces an all-filter labeled "all".

That's kinda flexible, but having to type out the exact filters you want only makes sense if the set is small and doesn't change much, and only doing substring-matching against playlist names is a pretty limited scope.
So the other way you can configure filters is by writing a Dactal query. It has to start with playlisted, which gets you the list of all the tracks from all the indexed playlists.

It has to end with groups of those tracks.

The groups are the filter choices. My query takes the playlist name, splits it at the comma to extract the date, pulls the year out of that date, groups by that year, and sorts the resulting year-groups in numeric order. But as long as your query starts with "playlisted" and ends with groups, in between it can do whatever you want. Once you have it working your way, just copy it into the "filter" box:

The magic "all" filter is added automatically if you're using a query. I should probably add an option to control that, but I haven't yet. This gets us back to:

...except dynamically, now, so I won't have to remember to add 2026 by hand, it will just appear when needed. Assuming, bravely, that neither AI nor fascists have consumed us before then.
If Curio were a commercial application, surely we would never ship a feature anywhere near this awkward and unguarded. But it isn't, and "we" is me, and I'm trying to imagine what the world could be like if your software invited you to be awkward and unguarded instead of pandered to; curious instead of customers.
PS: Also...

¶ 17 April 2025
The only excuse for not rejecting the Trump adminstration is that you don't believe they will come for you. And while it's true that they might not, they definitely would.
But, worse, the only excuse for supporting the Trump administration, as modeled relentlessly by its membership from top to bottom, is that you believe your identity is based on the entirely insane conviction that they wouldn't send you to a Salvadorean torture prison, and even that delusion gives you no jolt of imaginary self-esteem unless they are actively sending other equally-vulnerable people to Salvadorean torture prisons.
But, worse, the only excuse for supporting the Trump administration, as modeled relentlessly by its membership from top to bottom, is that you believe your identity is based on the entirely insane conviction that they wouldn't send you to a Salvadorean torture prison, and even that delusion gives you no jolt of imaginary self-esteem unless they are actively sending other equally-vulnerable people to Salvadorean torture prisons.
¶ Important Message · 29 January 2025
To all employees of the executive branch of the United States government with start dates on or after January 20, 2025:
I am writing to inform you that due to changing priorities your positions have been terminated, effective immediately.
Please return all federal coffee mugs to the kitchen areas before departing.
I am writing to inform you that due to changing priorities your positions have been terminated, effective immediately.
Please return all federal coffee mugs to the kitchen areas before departing.
¶ Query geekery motivated by music geekery · 27 January 2025 listen/tech
The listening-history tools in Curio include a thing for telling you the top genres from your listening year, because I think that's interesting.
Counting genres with Dactal, the query language in Curio, is easy. Or, at least, counting them in the simplest way is easy:
Take the list of artists (in this case the artists whose new 2024 songs you listened to in 2024), group them by genre, sort the genres by count.

Artists can and often do belong to multiple genres, though, so you might reasonably guess that some these overlap: symphonic metal and symphonic power metal; anime, j-rock, alt-idol, idol rock?
One very simple algorithm for reducing a set of overlapping categories to a smaller representative set is to take the genre with the most artists, then remove all the artists with that genre (whether they have other genres or not), then repeat. Dactal has a repeat operator for doing this kind of thing. We need a few other query features to make the query we need, but it's still fairly simple:
? is the Dactal start operator, which is implied at the beginning of a query and thus often doesn't actually appear at all, but here we use it to effectively interleave queries that keep track of the genres we've found and the artists we have left. We begin with all the artists and no genres, and then the indented subquery does two things:
- remove the artists from the last genre, using the set disjunction filter :-~~ (which does nothing the first time, because there are no genres yet)
- find the top genre for the artists we have left and add it to the existing list of topgenres
The ! repeat operator at the end of the subquery tells it to repeat the previous operation until it produces the same result twice (meaning there's nothing left to add), which happens for me after 139 iterations:
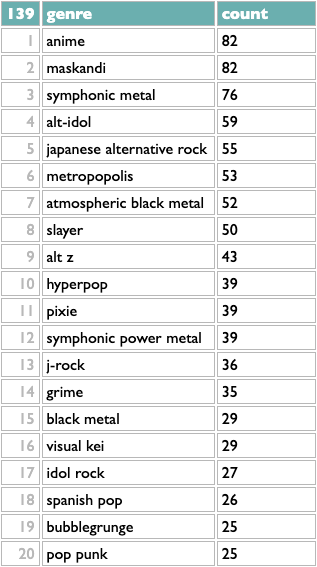
This is a little better. Flipping back and forth, I see that j-rock was 5th in the raw version, with 62 artists, but in the iterative version it drops to 13th, because only 36 of those 62 artists aren't part of any higher-ranked genres. Similarly, symphonic power metal drops from 6th to 12th. Japanese alternative rock moves up, because only 1 of those 56 artists was being double-counted before.
Really, though, this list of 139 "representative" genres still overstates the granularity into which my listening is emotionally organized. If you do not tend to use the words "granularity" and "emotionally" in the same sentences in your internal monologue, then you should probably cut your losses and tune out now. In order to cluster genres instead of just subsetting them, we need almost every major feature of Dactal:
I'm not going to claim this is "easy", but I've written variations on this algorithm in Ruby, Python, SQL and Javascript over the years, and I can tell you that all of those versions were much longer and involved way more punctuation than this, in addition to a lot more words that are about computers instead of about music.
The first two steps of the clustering are about the same as in the simpler version: eliminate any artists we've already used, and then find the top genre. Here we're scoring genres by summing up the square roots of artist points, instead of just counting artists, to measure a combination of listening breadth and listening depth, but that's added complexity in the question, not just the answer.
The clustering part is that once we have a top genre, we take all its artists and count their other genres, and then compare the overlap sizes with those genres' total artist counts (using lookups in the genre index created in the second line of the query). Other genres that overlap non-trivially with the first genre also get added to the cluster. Then the whole thing repeats. So instead of building a flat list of genres, this version builds a list of nested genre lists.
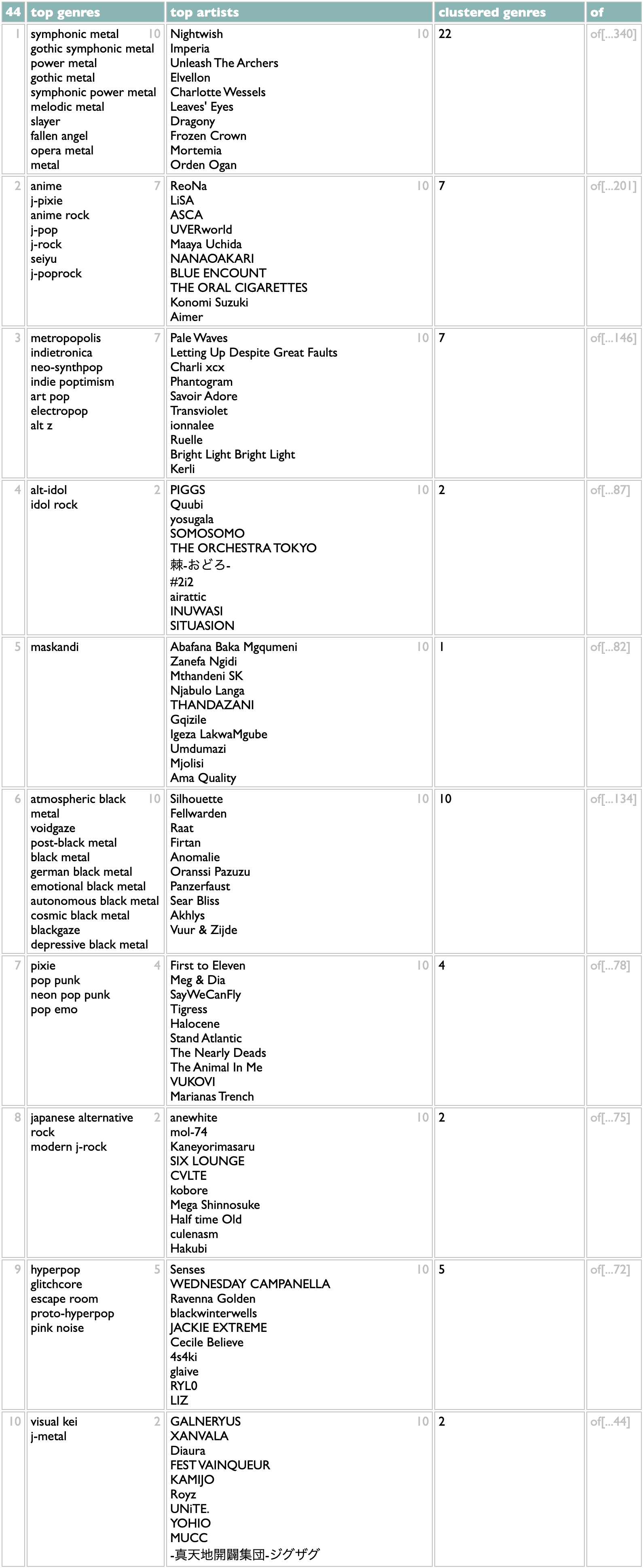
This is, for me, a lot closer to correct than the flat list, and certainly more interesting. It doesn't distribute my Japanese tastes exactly right (I don't care about anime, per se, so I usually put ReoNa and LiSA with the alt-idol groups for sonic reasons), but these first 10 statistical clusters are all aspects of my taste that I would list individually if you inadvisedly gave me an excuse, and of the 44 ways it breaks down my 2024, the only ones that get me thinking about override mechanics are towards the bottom where the genre data doesn't know that I tend to put the Spanish metal bands and the medieval rock nerds in with the other melodic metal styles.
If you want to try this on your own listening, there are now both "genres" and "genre clusters" views on the History page in Curio. But as with all of those, there is also a "see the query for this" at the bottom of the results, so if you want to experiment with variations, you can.
Although by you, as usual, I probably mean me. But by me I mean all of us.
Counting genres with Dactal, the query language in Curio, is easy. Or, at least, counting them in the simplest way is easy:
2024 artists scored/genre=(.artist.artist genres.genres)#count
Take the list of artists (in this case the artists whose new 2024 songs you listened to in 2024), group them by genre, sort the genres by count.

Artists can and often do belong to multiple genres, though, so you might reasonably guess that some these overlap: symphonic metal and symphonic power metal; anime, j-rock, alt-idol, idol rock?
One very simple algorithm for reducing a set of overlapping categories to a smaller representative set is to take the genre with the most artists, then remove all the artists with that genre (whether they have other genres or not), then repeat. Dactal has a repeat operator for doing this kind of thing. We need a few other query features to make the query we need, but it's still fairly simple:
artistsx=(2024 artists scored|genre=(.id.artist genres.genres))
?topgenres=()
?(
?artistsx=(artistsx:-~~(topgenres:@@1.of))
?topgenres=(topgenres,(artistsx/genre:count>=5#count:@1))
)!
?topgenres=()
?(
?artistsx=(artistsx:-~~(topgenres:@@1.of))
?topgenres=(topgenres,(artistsx/genre:count>=5#count:@1))
)!
? is the Dactal start operator, which is implied at the beginning of a query and thus often doesn't actually appear at all, but here we use it to effectively interleave queries that keep track of the genres we've found and the artists we have left. We begin with all the artists and no genres, and then the indented subquery does two things:
- remove the artists from the last genre, using the set disjunction filter :-~~ (which does nothing the first time, because there are no genres yet)
- find the top genre for the artists we have left and add it to the existing list of topgenres
The ! repeat operator at the end of the subquery tells it to repeat the previous operation until it produces the same result twice (meaning there's nothing left to add), which happens for me after 139 iterations:

This is a little better. Flipping back and forth, I see that j-rock was 5th in the raw version, with 62 artists, but in the iterative version it drops to 13th, because only 36 of those 62 artists aren't part of any higher-ranked genres. Similarly, symphonic power metal drops from 6th to 12th. Japanese alternative rock moves up, because only 1 of those 56 artists was being double-counted before.
Really, though, this list of 139 "representative" genres still overstates the granularity into which my listening is emotionally organized. If you do not tend to use the words "granularity" and "emotionally" in the same sentences in your internal monologue, then you should probably cut your losses and tune out now. In order to cluster genres instead of just subsetting them, we need almost every major feature of Dactal:
?artistsx=(2024 artists scored|genre=(.id.artist genres.genres),weight=(....artistpoints,sqrt))
?genre index=(artistsx/genre,of=artists:count>=5)
?clusters=()
?(
?artistsx=(artistsx:-~~(clusters:@@1.of))
?nextgenre=(artistsx/genre,of=artists:count>=10#(.artists....weight,total),count:@1)
?nextcluster=(
nextgenre.artists/genre,of=artists:count>=5
||total=(.genre.genre index.count),overlap=[=count/total]
:(.total) :overlap>=[.1] #(.artists....weight,total),count
...top genres=(.genre:@<=10),
top artists=(.artists:@<=10.name),
clustered genres=(.genre....count),
of=(.genre.genre index.artists)
:(.top genres)
)
?clusters=(clusters,nextcluster)
)!
?genre index=(artistsx/genre,of=artists:count>=5)
?clusters=()
?(
?artistsx=(artistsx:-~~(clusters:@@1.of))
?nextgenre=(artistsx/genre,of=artists:count>=10#(.artists....weight,total),count:@1)
?nextcluster=(
nextgenre.artists/genre,of=artists:count>=5
||total=(.genre.genre index.count),overlap=[=count/total]
:(.total) :overlap>=[.1] #(.artists....weight,total),count
...top genres=(.genre:@<=10),
top artists=(.artists:@<=10.name),
clustered genres=(.genre....count),
of=(.genre.genre index.artists)
:(.top genres)
)
?clusters=(clusters,nextcluster)
)!
I'm not going to claim this is "easy", but I've written variations on this algorithm in Ruby, Python, SQL and Javascript over the years, and I can tell you that all of those versions were much longer and involved way more punctuation than this, in addition to a lot more words that are about computers instead of about music.
The first two steps of the clustering are about the same as in the simpler version: eliminate any artists we've already used, and then find the top genre. Here we're scoring genres by summing up the square roots of artist points, instead of just counting artists, to measure a combination of listening breadth and listening depth, but that's added complexity in the question, not just the answer.
The clustering part is that once we have a top genre, we take all its artists and count their other genres, and then compare the overlap sizes with those genres' total artist counts (using lookups in the genre index created in the second line of the query). Other genres that overlap non-trivially with the first genre also get added to the cluster. Then the whole thing repeats. So instead of building a flat list of genres, this version builds a list of nested genre lists.

This is, for me, a lot closer to correct than the flat list, and certainly more interesting. It doesn't distribute my Japanese tastes exactly right (I don't care about anime, per se, so I usually put ReoNa and LiSA with the alt-idol groups for sonic reasons), but these first 10 statistical clusters are all aspects of my taste that I would list individually if you inadvisedly gave me an excuse, and of the 44 ways it breaks down my 2024, the only ones that get me thinking about override mechanics are towards the bottom where the genre data doesn't know that I tend to put the Spanish metal bands and the medieval rock nerds in with the other melodic metal styles.
If you want to try this on your own listening, there are now both "genres" and "genre clusters" views on the History page in Curio. But as with all of those, there is also a "see the query for this" at the bottom of the results, so if you want to experiment with variations, you can.
Although by you, as usual, I probably mean me. But by me I mean all of us.
¶ What we know · 14 January 2025 listen/tech
The thing I worked on the longest, in my Echo Nest / Spotify time, was calculating artist similarity. In the Echo Nest days, when we didn't have direct listening data, we derived scores for pairs of artists based on patterns of shared descriptive words found in web pages about each of them. Or, more accurately, web pages maybe about them, because figuring out whether any given blob of text that contains a given string of letters is about a band whose name is that same string of letters, at all never mind in a descriptively useful sense, is hard.
Once we got swallowed by Spotify, of course, we had all the listening-data plankton we could krill. The goal of "collaborative filtering", taken most lowercasely, is to extract collective knowledge from collected data. The Spotify feature this work powered was called (eventually) Fans Also Like, and one of my greatest organizational triumphs at Spotify was that after many years of technical work and political lobbying, I succeeded in making this feature live up to its name. For about a year and a half, starting around April 2023, the Spotify artist page Fans Also Like lists were really an algebraic formulation of getting each artist's fans, not just listeners, and finding out what other artists they disproportionately also liked. And nothing else. You only saw the first 20 results for each artist, but the underlying dataset behind this went deeper, and I think was a genuinely unprecedented collective cultural achievement of the Spotify audience.
Most of the complexity of doing this well, if by "well" you mean reflecting actual patterns of human interest as opposed to round-off error in vector embeddings or clandestine margin-chiseling, which you should, was actually in the quantification of "fan". I would not be able to explain all the details of that process from memory, even if I were allowed to, but the core idea is that the more you raise the threshold of fandom, the better similarity signal you get from the listening patterns of those fans, but the fewer artists are included, so if you want both precision and recall, you have to get creative.
And of course you have to get data, to begin with. We cannot recreate the lost Fans Also Like network from outside of Spotify, because we cannot get their dataset of fan/artist pairs. Or, really, our dataset, because it's our listening.
If you happen to have pairs of any kind of data, though, doing simple math to extract similarity of one half of those pairs based on the co-reference patterns of the other half is easy. In fact, if you have that pair data in JSON, you can load it into the spec/doc/test/playground page for Dactal and do it right now.
For example, over at AlbumOfTheYear.org they aggregate album-of-the-year lists from many other publications and produce a scored meta-ranking of the year's albums. But this dataset of publication/album pairs also encodes patterns of implicit knowledge about album similarity based on the tendencies of publications to list albums together, and about publication similarity based on the tendencies of albums to appeal to publications together.
Here's how to extract it using Dactal:
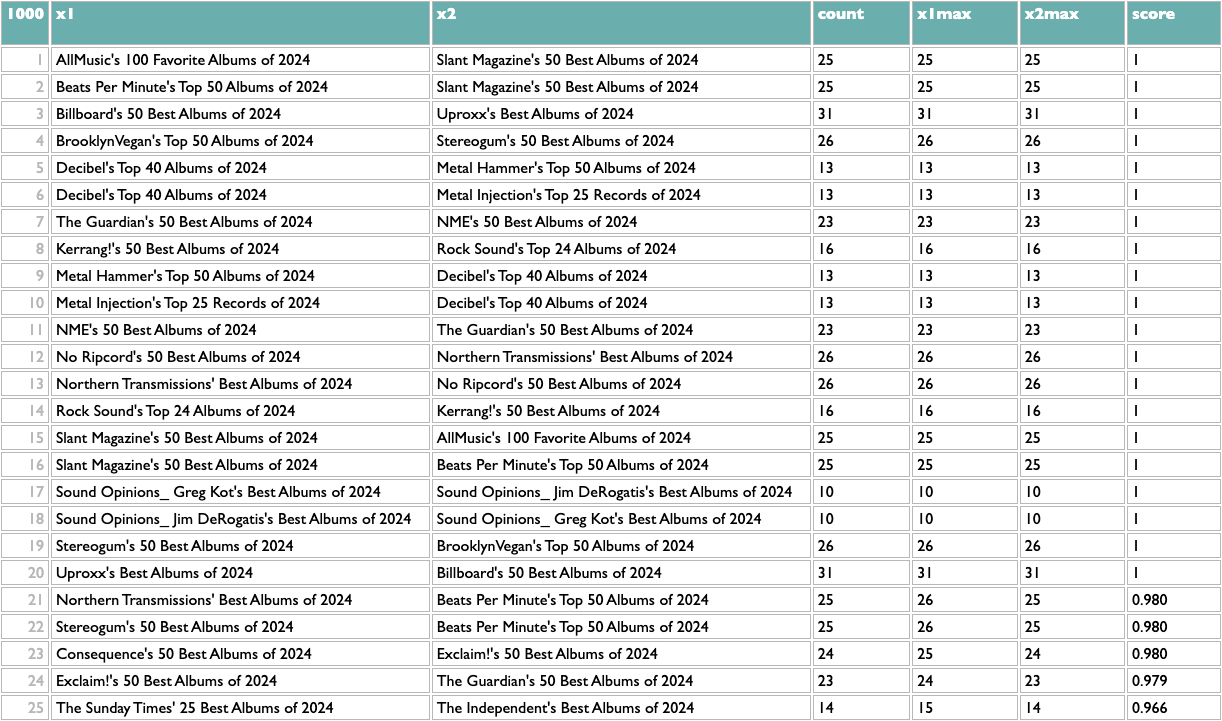
The first orange line is specific to this data, my extraction from the AOTY lists, but all it needs to produce is a two-column list with x and y. Like this:
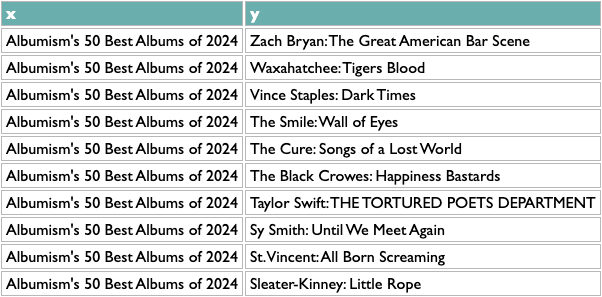
Once you have any x/y list like this, the rest of the query works the same. The scoring logic here (which isn't what I used at Spotify, but you probably aren't dealing with 600 million people listening to 10 million artists) counts the overlap between any pair of x based on y, and then scales that by the maximum overlaps of both parts of the pair. So a score of 1 means that both things in that pair are each other's closest match. The calculation is asymmetric because one part of a pair may be the other's closest match but not vice versa. If you read about music online you may know that, e.g., Decibel and Metal Hammer are both metal-specific, The Guardian and NME are both British, and BrooklynVegan and Stereogum are both read by the kind of people who read BrooklynVegan and Stereogum, so the top of those results passes a basic sanity check.
And because everything but the first line is independent of what x and y are, that means we can flip x and y (just those two letters!) and get album similarity:
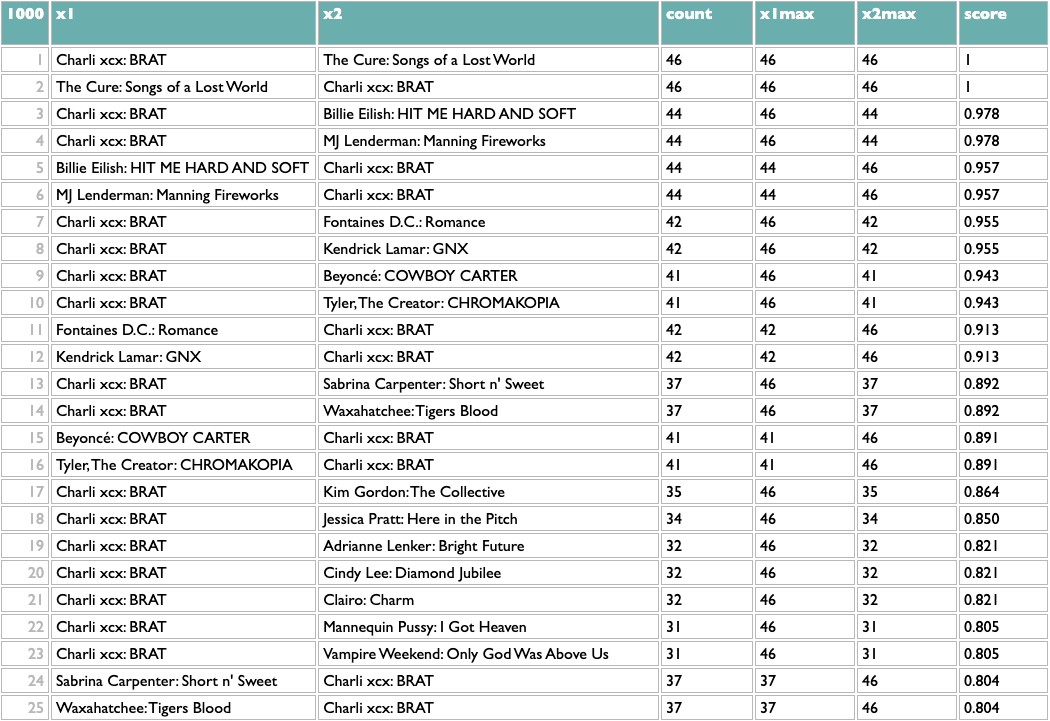
This passes a sanity check – everybody who writes about music likes Charli – but not an interestingness check, so we might opt to filter out BRAT just to see what else we can learn:
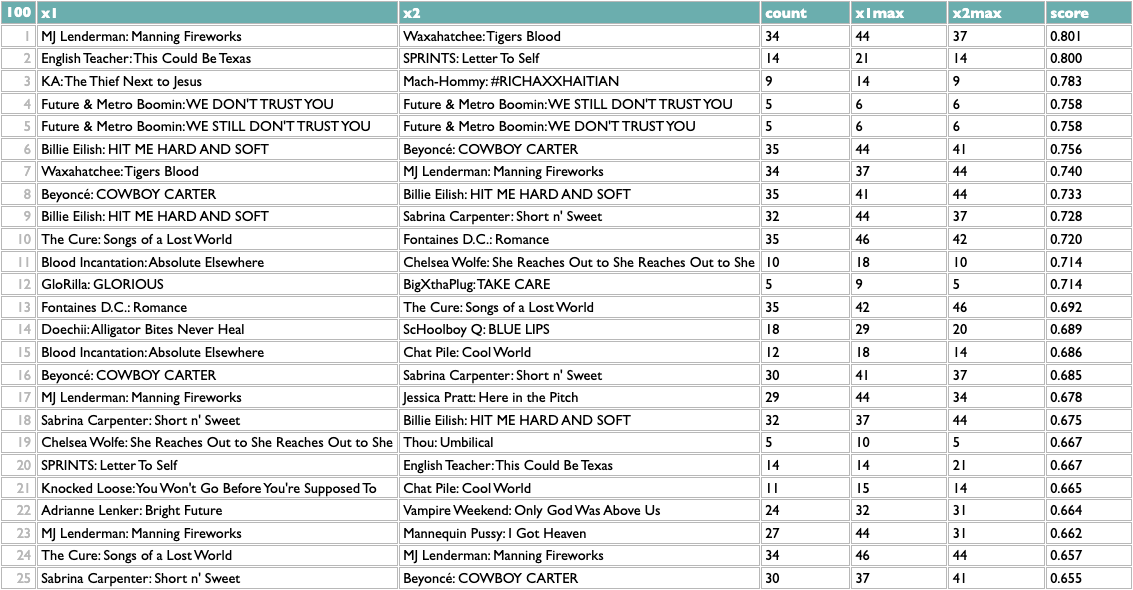
Not bad! The two Future/Metro Boomin albums are most similar to each other, which is the good kind of confidence-boosting boring answer, but a bunch of the other pairs are plausible yet non-obvious: two indie rock records, two UK indie guitar records, two indie rappers, two metal-adjacent records.
These scores are normalized locally, not globally, so the real way to use them is to reorganize this by album. Which is also easy:
That's interesting to me. What's interesting to you?
[PS: Oh, here, I put this dataset up in raw interactive form, so you can play with it yourself if you want.]
Once we got swallowed by Spotify, of course, we had all the listening-data plankton we could krill. The goal of "collaborative filtering", taken most lowercasely, is to extract collective knowledge from collected data. The Spotify feature this work powered was called (eventually) Fans Also Like, and one of my greatest organizational triumphs at Spotify was that after many years of technical work and political lobbying, I succeeded in making this feature live up to its name. For about a year and a half, starting around April 2023, the Spotify artist page Fans Also Like lists were really an algebraic formulation of getting each artist's fans, not just listeners, and finding out what other artists they disproportionately also liked. And nothing else. You only saw the first 20 results for each artist, but the underlying dataset behind this went deeper, and I think was a genuinely unprecedented collective cultural achievement of the Spotify audience.
Most of the complexity of doing this well, if by "well" you mean reflecting actual patterns of human interest as opposed to round-off error in vector embeddings or clandestine margin-chiseling, which you should, was actually in the quantification of "fan". I would not be able to explain all the details of that process from memory, even if I were allowed to, but the core idea is that the more you raise the threshold of fandom, the better similarity signal you get from the listening patterns of those fans, but the fewer artists are included, so if you want both precision and recall, you have to get creative.
And of course you have to get data, to begin with. We cannot recreate the lost Fans Also Like network from outside of Spotify, because we cannot get their dataset of fan/artist pairs. Or, really, our dataset, because it's our listening.
If you happen to have pairs of any kind of data, though, doing simple math to extract similarity of one half of those pairs based on the co-reference patterns of the other half is easy. In fact, if you have that pair data in JSON, you can load it into the spec/doc/test/playground page for Dactal and do it right now.
For example, over at AlbumOfTheYear.org they aggregate album-of-the-year lists from many other publications and produce a scored meta-ranking of the year's albums. But this dataset of publication/album pairs also encodes patterns of implicit knowledge about album similarity based on the tendencies of publications to list albums together, and about publication similarity based on the tendencies of albums to appeal to publications together.
Here's how to extract it using Dactal:
?data=(aoty.entries.(....x=aotylist,y=albumkey))
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
#score
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
#score

The first orange line is specific to this data, my extraction from the AOTY lists, but all it needs to produce is a two-column list with x and y. Like this:
?data=(aoty.entries.(....x=aotylist,y=albumkey))

Once you have any x/y list like this, the rest of the query works the same. The scoring logic here (which isn't what I used at Spotify, but you probably aren't dealing with 600 million people listening to 10 million artists) counts the overlap between any pair of x based on y, and then scales that by the maximum overlaps of both parts of the pair. So a score of 1 means that both things in that pair are each other's closest match. The calculation is asymmetric because one part of a pair may be the other's closest match but not vice versa. If you read about music online you may know that, e.g., Decibel and Metal Hammer are both metal-specific, The Guardian and NME are both British, and BrooklynVegan and Stereogum are both read by the kind of people who read BrooklynVegan and Stereogum, so the top of those results passes a basic sanity check.
And because everything but the first line is independent of what x and y are, that means we can flip x and y (just those two letters!) and get album similarity:
?data=(aoty.entries.(....y=aotylist,x=albumkey))
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
#score
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
#score

This passes a sanity check – everybody who writes about music likes Charli – but not an interestingness check, so we might opt to filter out BRAT just to see what else we can learn:
?data=(aoty.entries.(....y=aotylist,x=albumkey))
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
:-(.x1,x2:=[Charli xcx: BRAT])
#score
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
:-(.x1,x2:=[Charli xcx: BRAT])
#score

Not bad! The two Future/Metro Boomin albums are most similar to each other, which is the good kind of confidence-boosting boring answer, but a bunch of the other pairs are plausible yet non-obvious: two indie rock records, two UK indie guitar records, two indie rappers, two metal-adjacent records.
These scores are normalized locally, not globally, so the real way to use them is to reorganize this by album. Which is also easy:
?data=(aoty.entries.(....y=aotylist,x=albumkey))
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
:-(.x1,x2:=[Charli xcx: BRAT])
#score
/iyl=(.x1,x2)
.(....iyl,yml=(._,(.of.x1,x2):@>1:@<=10)
?paircounts=(data/y/x1=(.of.x),x2=(.of.x):(.key:@2):count>=5)
?x maxpoints=(paircounts/key||maxpoints=(.of.count....max))
?paircounts
||x1max=(.x1.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
x2max=(.x2.x maxpoints.maxpoints),
score=[=2*count**2/((count+x1max)*x2max)]
:-(.x1,x2:=[Charli xcx: BRAT])
#score
/iyl=(.x1,x2)
.(....iyl,yml=(._,(.of.x1,x2):@>1:@<=10)
| 146 | iyl | yml |
| 1 | A. G. Cook: Britpop | 10 Maggie Rogers: Don't Forget Me Remi Wolf: Big Ideas Clairo: Charm Jack White: No Name Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Fontaines D.C.: Romance Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS |
| 2 | Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future | 10 Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Fontaines D.C.: Romance Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Kim Gordon: The Collective Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Floating Points: Cascade Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 3 | Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness | 10 English Teacher: This Could Be Texas The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Bob Vylan: Humble As The Sun Hamish Hawk: A Firmer Hand IDLES: TANGK SPRINTS: Letter To Self Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Wunderhorse: Midas |
| 4 | Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine | 10 Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Dua Lipa: Radical Optimism Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Kacey Musgraves: Deeper Well Clairo: Charm Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 5 | Arooj Aftab: Night Reign | 10 Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor |
| 6 | Astrid Sonne: Great Doubt | 4 Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police |
| 7 | Being Dead: EELS | 10 This Is Lorelei: Box For Buddy, Box For Star Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Clairo: Charm |
| 8 | Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Kim Gordon: The Collective Julia Holter: Something in the Room She Moves Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Chat Pile: Cool World |
| 9 | Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER | 10 Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Kendrick Lamar: GNX Jack White: No Name The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS |
| 10 | BigXthaPlug: TAKE CARE | 4 GloRilla: GLORIOUS Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX |
| 11 | Bill Ryder-Jones: Iechyd Da | 10 Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Fontaines D.C.: Romance Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Kim Gordon: The Collective Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee |
| 12 | Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT | 10 Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Clairo: Charm St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine Kendrick Lamar: GNX Taylor Swift: THE TORTURED POETS DEPARTMENT Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS |
| 13 | Bladee: Cold Visions | 2 Mount Eerie: Night Palace Clairo: Charm |
| 14 | Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere | 10 Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She Chat Pile: Cool World Judas Priest: Invincible Shield Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Opeth: The Last Will and Testament Gatecreeper: Dark Superstition Thou: Umbilical Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future |
| 15 | Bob Vylan: Humble As The Sun | Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness |
| 16 | Bring Me The Horizon: POST HUMAN: NeX GEn | Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To |
| 17 | Brittany Howard: What Now | 10 Common & Pete Rock: The Auditorium Vol. 1 Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER E L U C I D: REVELATOR ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Johnny Blue Skies: Passage du Desir |
| 18 | Caribou: Honey | 3 Kim Gordon: The Collective Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 19 | Cassandra Jenkins: My Light, My Destroyer | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Kim Gordon: The Collective Mabe Fratti: Sentir Que No Sabes Arooj Aftab: Night Reign The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police |
| 20 | Chanel Beads: Your Day Will Come | 5 Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 21 | Charli xcx: Brat and it's completely different but also still brat | 5 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Kim Gordon: The Collective |
| 22 | Chat Pile: Cool World | 10 Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Gouge Away: Deep Sage Touché Amoré: Spiral in a Straight Line Foxing: Foxing Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Mount Eerie: Night Palace The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 23 | Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She | 10 Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Thou: Umbilical Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Touché Amoré: Spiral in a Straight Line Geordie Greep: The New Sound Julia Holter: Something in the Room She Moves Chat Pile: Cool World Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven |
| 24 | Chief Keef: Almighty So 2 | 10 Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Clairo: Charm Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Kendrick Lamar: GNX Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 25 | Christopher Owens: I Wanna Run Barefoot Through Your Hair | 4 Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 26 | Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Mount Eerie: Night Palace Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Kim Gordon: The Collective |
| 27 | claire rousay: sentiment | 10 Kim Gordon: The Collective Arooj Aftab: Night Reign MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Clairo: Charm Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 28 | Clairo: Charm | 10 Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police St. Vincent: All Born Screaming MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Fontaines D.C.: Romance Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet |
| 29 | Clarissa Connelly: World of Work | 2 Kim Gordon: The Collective Nala Sinephro: Endlessness |
| 30 | Common & Pete Rock: The Auditorium Vol. 1 | 6 Vince Staples: Dark Times Brittany Howard: What Now ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 31 | Confidence Man: 3AM (LA LA LA) | 5 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Fontaines D.C.: Romance |
| 32 | The Cure: Songs of a Lost World | 10 Fontaines D.C.: Romance MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jack White: No Name Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven |
| 33 | Denzel Curry: King of the Mischievous South Vol. 2 | 2 Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA |
| 34 | DIIV: Frog in Boiling Water | 10 Father John Misty: Mahashmashana Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Fontaines D.C.: Romance Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Clairo: Charm Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet |
| 35 | Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal | 10 ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Kendrick Lamar: GNX Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA GloRilla: GLORIOUS MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police |
| 36 | Dua Lipa: Radical Optimism | 10 St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Clairo: Charm The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 37 | E L U C I D: REVELATOR | 10 Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Brittany Howard: What Now Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal |
| 38 | Ekko Astral: pink balloons | 10 Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Fontaines D.C.: Romance Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 39 | Empress Of: For Your Consideration | 10 Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Clairo: Charm Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Jack White: No Name Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Kim Gordon: The Collective Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 40 | English Teacher: This Could Be Texas | 10 SPRINTS: Letter To Self The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Wunderhorse: Midas Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood |
| 41 | Erika de Casier: Still | 3 Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 42 | Ezra Collective: Dance, No One's Watching | 5 Jamie xx: In Waves MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Fontaines D.C.: Romance |
| 43 | Fabiana Palladino: Fabiana Palladino | 10 Tyla: TYLA Nala Sinephro: Endlessness MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Kim Gordon: The Collective Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God Jamie xx: In Waves Fontaines D.C.: Romance Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood |
| 44 | Fat Dog: WOOF. | 2 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy St. Vincent: All Born Screaming |
| 45 | Father John Misty: Mahashmashana | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Wild Pink: Dulling The Horns The Cure: Songs of a Lost World DIIV: Frog in Boiling Water Gouge Away: Deep Sage Fontaines D.C.: Romance Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Kendrick Lamar: GNX |
| 46 | Faye Webster: Underdressed at the Symphony | 2 Clairo: Charm Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 47 | Fievel Is Glauque: Rong Weicknes | Kim Gordon: The Collective |
| 48 | Floating Points: Cascade | 10 Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Julia Holter: Something in the Room She Moves Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Mount Eerie: Night Palace Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Brittany Howard: What Now Johnny Blue Skies: Passage du Desir |
| 49 | Fontaines D.C.: Romance | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness |
| 50 | Foxing: Foxing | 5 Chat Pile: Cool World Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Kendrick Lamar: GNX MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 51 | Friko: Where we've been, Where we go from here | 4 Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 52 | Future & Metro Boomin: WE DON'T TRUST YOU | 9 Future & Metro Boomin: WE STILL DON'T TRUST YOU Vince Staples: Dark Times ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER |
| 53 | Future & Metro Boomin: WE STILL DON'T TRUST YOU | 6 Future & Metro Boomin: WE DON'T TRUST YOU Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police |
| 54 | Gatecreeper: Dark Superstition | Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere |
| 55 | Geordie Greep: The New Sound | 10 Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She JPEGMAFIA: I LAY DOWN MY LIFE FOR YOU Julia Holter: Something in the Room She Moves Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Brittany Howard: What Now Mount Eerie: Night Palace Kim Gordon: The Collective Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown |
| 56 | Gillian Welch & David Rawlings: Woodland | 10 Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Hurray for the Riff Raff: The Past Is Still Alive Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Brittany Howard: What Now Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 57 | GloRilla: GLORIOUS | 10 BigXthaPlug: TAKE CARE ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Tyla: TYLA Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 58 | Godspeed You! Black Emperor: “NO TITLE AS OF 13 FEBRUARY 2024 28,340 DEAD” | 10 Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Kim Gordon: The Collective Vince Staples: Dark Times English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Mount Eerie: Night Palace The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Jack White: No Name |
| 59 | Gouge Away: Deep Sage | 10 High Vis: Guided Tour Chat Pile: Cool World Father John Misty: Mahashmashana Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 60 | Gracie Abrams: The Secret of Us | 5 Kacey Musgraves: Deeper Well Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER |
| 61 | Green Day: Saviors | The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 62 | Hamish Hawk: A Firmer Hand | 2 Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 63 | The Hard Quartet: The Hard Quartet | 4 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 64 | High Vis: Guided Tour | 4 Gouge Away: Deep Sage Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 65 | Hovvdy: Hovvdy | 10 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Father John Misty: Mahashmashana Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER |
| 66 | Hurray for the Riff Raff: The Past Is Still Alive | 10 Mount Eerie: Night Palace MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Gillian Welch & David Rawlings: Woodland KA: The Thief Next to Jesus Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 67 | IDLES: TANGK | 10 Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness The Cure: Songs of a Lost World SPRINTS: Letter To Self The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Fontaines D.C.: Romance Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA KNEECAP: Fine Art Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown English Teacher: This Could Be Texas |
| 68 | Jack White: No Name | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Kendrick Lamar: GNX Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jamie xx: In Waves Fontaines D.C.: Romance |
| 69 | Jamie xx: In Waves | 10 Fontaines D.C.: Romance Justice: Hyperdrama Jack White: No Name The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Yard Act: Where's My Utopia? MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 70 | Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Kim Gordon: The Collective Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal |
| 71 | Jlin: Akoma | 6 Mabe Fratti: Sentir Que No Sabes Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Kim Gordon: The Collective Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 72 | Johnny Blue Skies: Passage du Desir | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Brittany Howard: What Now Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jack White: No Name Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven |
| 73 | JPEGMAFIA: I LAY DOWN MY LIFE FOR YOU | 10 Geordie Greep: The New Sound Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Kim Gordon: The Collective Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Kendrick Lamar: GNX Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch |
| 74 | Judas Priest: Invincible Shield | Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere |
| 75 | Julia Holter: Something in the Room She Moves | 10 Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She Floating Points: Cascade Geordie Greep: The New Sound Mount Eerie: Night Palace Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Kim Gordon: The Collective The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 76 | Justice: Hyperdrama | 3 Jamie xx: In Waves Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 77 | KA: The Thief Next to Jesus | 10 Mach-Hommy: #RICHAXXHAITIAN Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Mount Eerie: Night Palace LL COOL J: THE FORCE Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Hurray for the Riff Raff: The Past Is Still Alive Kim Gordon: The Collective MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere |
| 78 | Kacey Musgraves: Deeper Well | 10 Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Gracie Abrams: The Secret of Us Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Taylor Swift: THE TORTURED POETS DEPARTMENT Kendrick Lamar: GNX Jack White: No Name Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 79 | Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS | 10 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Tyla: TYLA Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Clairo: Charm Ekko Astral: pink balloons Empress Of: For Your Consideration Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet |
| 80 | Kamasi Washington: Fearless Movement | 4 Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 81 | KAYTRANADA: Timeless | 3 Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 82 | Kelly Lee Owens: Dreamstate | 10 Nia Archives: Silence Is Loud SPRINTS: Letter To Self Tyla: TYLA English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Clairo: Charm Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Fontaines D.C.: Romance |
| 83 | Kendrick Lamar: GNX | 10 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Jack White: No Name MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Vince Staples: Dark Times Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet |
| 84 | Kim Deal: Nobody Loves You More | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Fontaines D.C.: Romance MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future |
| 85 | Kim Gordon: The Collective | 10 Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Mount Eerie: Night Palace Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor |
| 86 | KNEECAP: Fine Art | 10 Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness IDLES: TANGK English Teacher: This Could Be Texas St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Clairo: Charm |
| 87 | Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To | 10 Chat Pile: Cool World Bring Me The Horizon: POST HUMAN: NeX GEn Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Lip Critic: Hex Dealer Touché Amoré: Spiral in a Straight Line Foxing: Foxing Zach Bryan: The Great American Bar Scene Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 88 | The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy | 10 English Teacher: This Could Be Texas St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Fontaines D.C.: Romance Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness Wunderhorse: Midas Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat |
| 89 | Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat | 10 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Kim Gordon: The Collective Los Campesinos!: All Hell Nadine Shah: Filthy Underneath Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk SPRINTS: Letter To Self The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 90 | The Lemon Twigs: A Dream Is All We Know | 2 Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Kim Gordon: The Collective |
| 91 | Lime Garden: One More Thing | 2 English Teacher: This Could Be Texas The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy |
| 92 | Lip Critic: Hex Dealer | 3 Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Fontaines D.C.: Romance |
| 93 | Liquid Mike: Paul Bunyan's Slingshot | 2 Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 94 | LL COOL J: THE FORCE | 6 Mach-Hommy: #RICHAXXHAITIAN KA: The Thief Next to Jesus Kendrick Lamar: GNX Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA |
| 95 | Los Campesinos!: All Hell | 10 Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat Arooj Aftab: Night Reign English Teacher: This Could Be Texas The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Fontaines D.C.: Romance Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee |
| 96 | Mabe Fratti: Sentir Que No Sabes | 10 Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Jlin: Akoma Cassandra Jenkins: My Light, My Destroyer Arooj Aftab: Night Reign MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Kim Gordon: The Collective Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Chat Pile: Cool World Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee |
| 97 | Mach-Hommy: #RICHAXXHAITIAN | 10 KA: The Thief Next to Jesus LL COOL J: THE FORCE Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Chat Pile: Cool World Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police |
| 98 | Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk | 10 Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Vince Staples: Dark Times Kim Gordon: The Collective English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Chat Pile: Cool World |
| 99 | Maggie Rogers: Don't Forget Me | 10 Vince Staples: Dark Times A. G. Cook: Britpop Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Jack White: No Name ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Taylor Swift: THE TORTURED POETS DEPARTMENT Kendrick Lamar: GNX Clairo: Charm Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS |
| 100 | Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Fontaines D.C.: Romance Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Mount Eerie: Night Palace Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee |
| 101 | The Marías: Submarine | 4 Clairo: Charm The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA |
| 102 | Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch MIKE & Tony Seltzer: Pinball Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Arooj Aftab: Night Reign E L U C I D: REVELATOR Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Jack White: No Name The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Kim Gordon: The Collective |
| 103 | Michael Kiwanuka: Small Changes | 3 Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness The Cure: Songs of a Lost World The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy |
| 104 | MIKE & Tony Seltzer: Pinball | 4 Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 105 | MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks | 10 Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Father John Misty: Mahashmashana Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Fontaines D.C.: Romance Mdou Moctar: Funeral for Justice Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor |
| 106 | Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Clairo: Charm Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Fontaines D.C.: Romance Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Tems: Born in the Wild |
| 107 | Mount Eerie: Night Palace | 10 Kim Gordon: The Collective Hurray for the Riff Raff: The Past Is Still Alive Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Bladee: Cold Visions Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Chat Pile: Cool World KA: The Thief Next to Jesus Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Floating Points: Cascade |
| 108 | Mustafa: Dunya | 10 Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Kendrick Lamar: GNX Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 109 | Nadine Shah: Filthy Underneath | 10 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness Kim Gordon: The Collective English Teacher: This Could Be Texas St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us |
| 110 | Nala Sinephro: Endlessness | 10 Mabe Fratti: Sentir Que No Sabes Kim Gordon: The Collective Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Cassandra Jenkins: My Light, My Destroyer Still House Plants: If I don't make it, I love u E L U C I D: REVELATOR Jlin: Akoma MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Chanel Beads: Your Day Will Come |
| 111 | Nia Archives: Silence Is Loud | 10 Kelly Lee Owens: Dreamstate Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events Tyla: TYLA The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness SPRINTS: Letter To Self English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Nala Sinephro: Endlessness |
| 112 | Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Fontaines D.C.: Romance St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Jamie xx: In Waves Kim Deal: Nobody Loves You More Jack White: No Name |
| 113 | Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Cassandra Jenkins: My Light, My Destroyer Kim Gordon: The Collective Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven |
| 114 | Nubya Garcia: ODYSSEY | The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 115 | NxWorries: WHY LAWD? | 8 Vince Staples: Dark Times ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Kendrick Lamar: GNX Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 116 | Opeth: The Last Will and Testament | Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere |
| 117 | Pet Shop Boys: Nonetheless | 2 Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 118 | Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events | 10 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Nia Archives: Silence Is Loud Wunderhorse: Midas English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness SPRINTS: Letter To Self Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Clairo: Charm |
| 119 | Ravyn Lenae: Bird's Eye | 2 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven |
| 120 | Rema: HEIS | 10 Tems: Born in the Wild Tyla: TYLA Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 121 | Remi Wolf: Big Ideas | 10 St. Vincent: All Born Screaming A. G. Cook: Britpop Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Clairo: Charm Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood |
| 122 | Rosali: Bite Down | 4 Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 123 | Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet | 10 Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Taylor Swift: THE TORTURED POETS DEPARTMENT Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine Kacey Musgraves: Deeper Well MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Tyla: TYLA Kendrick Lamar: GNX Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk |
| 124 | ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS | 10 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Vince Staples: Dark Times GloRilla: GLORIOUS Kendrick Lamar: GNX Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Future & Metro Boomin: WE DON'T TRUST YOU NxWorries: WHY LAWD? The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER |
| 125 | Shabaka: Perceive Its Beauty, Acknowledge Its Grace | Kim Gordon: The Collective |
| 126 | The Smile: Wall of Eyes | 10 The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor St. Vincent: All Born Screaming Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven |
| 127 | SPRINTS: Letter To Self | 10 English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness IDLES: TANGK Wunderhorse: Midas The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Kelly Lee Owens: Dreamstate Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events Nia Archives: Silence Is Loud Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk |
| 128 | St. Vincent: All Born Screaming | 10 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Dua Lipa: Radical Optimism The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds: Wild God Clairo: Charm Fontaines D.C.: Romance Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood |
| 129 | Still House Plants: If I don't make it, I love u | 10 Nala Sinephro: Endlessness Kim Gordon: The Collective Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Arooj Aftab: Night Reign Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee |
| 130 | Taylor Swift: THE TORTURED POETS DEPARTMENT | 10 Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Maggie Rogers: Don't Forget Me The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Kacey Musgraves: Deeper Well Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Ariana Grande: eternal sunshine Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events |
| 131 | Tems: Born in the Wild | 10 Rema: HEIS Tyla: TYLA Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Clairo: Charm Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Kendrick Lamar: GNX |
| 132 | This Is Lorelei: Box For Buddy, Box For Star | 10 Wild Pink: Dulling The Horns Being Dead: EELS Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Nilüfer Yanya: My Method Actor Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk |
| 133 | Thou: Umbilical | 4 Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS The Cure: Songs of a Lost World |
| 134 | Tierra Whack: WORLD WIDE WHACK | 4 Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 135 | Touché Amoré: Spiral in a Straight Line | 10 Chat Pile: Cool World Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Chelsea Wolfe: She Reaches Out to She Reaches Out to She The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Blood Incantation: Absolute Elsewhere Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA Fontaines D.C.: Romance Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood |
| 136 | Tyla: TYLA | 10 Rema: HEIS Tems: Born in the Wild Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Kali Uchis: ORQUÍDEAS Fabiana Palladino: Fabiana Palladino Nia Archives: Silence Is Loud Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal GloRilla: GLORIOUS ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Kelly Lee Owens: Dreamstate |
| 137 | Tyler, The Creator: CHROMAKOPIA | 10 ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Mk.gee: Two Star & The Dream Police Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Kendrick Lamar: GNX Jack White: No Name |
| 138 | Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us | 10 Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Jack White: No Name Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Father John Misty: Mahashmashana Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Laura Marling: Patterns in Repeat |
| 139 | Vince Staples: Dark Times | 10 ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Common & Pete Rock: The Auditorium Vol. 1 Future & Metro Boomin: WE DON'T TRUST YOU NxWorries: WHY LAWD? Maggie Rogers: Don't Forget Me Kendrick Lamar: GNX Doechii: Alligator Bites Never Heal Jack White: No Name Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER |
| 140 | Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood | 10 MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Kim Gordon: The Collective Jessica Pratt: Here in the Pitch Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future Cindy Lee: Diamond Jubilee Fontaines D.C.: Romance Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us |
| 141 | Wild Pink: Dulling The Horns | 8 This Is Lorelei: Box For Buddy, Box For Star Father John Misty: Mahashmashana Magdalena Bay: Imaginal Disk Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Waxahatchee: Tigers Blood Fontaines D.C.: Romance |
| 142 | Wishy: Triple Seven | 3 Mannequin Pussy: I Got Heaven Fontaines D.C.: Romance MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 143 | Wunderhorse: Midas | 8 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy English Teacher: This Could Be Texas Rachel Chinouriri: What A Devastating Turn of Events Amyl and The Sniffers: Cartoon Darkness SPRINTS: Letter To Self Fontaines D.C.: Romance The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT |
| 144 | Yard Act: Where's My Utopia? | 8 The Last Dinner Party: Prelude to Ecstasy Jamie xx: In Waves Beth Gibbons: Lives Outgrown Fontaines D.C.: Romance Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Adrianne Lenker: Bright Future MJ Lenderman: Manning Fireworks |
| 145 | Yasmin Williams: Acadia | 2 ScHoolboy Q: BLUE LIPS Vampire Weekend: Only God Was Above Us |
| 146 | Zach Bryan: The Great American Bar Scene | 6 Knocked Loose: You Won't Go Before You're Supposed To Kendrick Lamar: GNX Billie Eilish: HIT ME HARD AND SOFT The Cure: Songs of a Lost World Sabrina Carpenter: Short n' Sweet Beyoncé: COWBOY CARTER |
That's interesting to me. What's interesting to you?
[PS: Oh, here, I put this dataset up in raw interactive form, so you can play with it yourself if you want.]
For anybody interested in the particular subgeekery of language design, I thought of five potential ways to address the Dactal usability issue of
1. Try to embrace the weirdness. This is always my first discipline. Don't be too quick to treat every weirdness as a problem that has to be solved. Some things are weird compared to outside references, but normal in a new system's internal logic. If a weirdness is really a conceptual inconsistency, embracing it will keep feeling awkward no matter how many times you do it. In this case, I think the most persuasive critique is that Dactal tries to keep the human language of queries in the vocabulary of the data, not the system, and the mechanics in punctuation, but "of" is uneasily poised somewhere between the two. You can work out what
2. Use the tools you already have. Dactal already has a way to create additional properties. So if we want to group tracks by artist and then be able to get back to the grouped tracks with "tracks" instead of saying "of", we can just do this:
3. If we're going to explore adding a new feature to grouping to handling this idea directly, we could just move "tracks=of" from a separate annotation (|) operation into the grouping operation:
4. Doing the relabeling with the same syntax in the other order, however, like:
5. I implemented #4, but I do keep coming back to #2 in my mind. It might be generally useful to have a way of renaming existing properties instead of just duplicating them. Or a way of deleting them, for that matter. So I also implemented
.of.of:=where are we?.of
being hard to follow.
1. Try to embrace the weirdness. This is always my first discipline. Don't be too quick to treat every weirdness as a problem that has to be solved. Some things are weird compared to outside references, but normal in a new system's internal logic. If a weirdness is really a conceptual inconsistency, embracing it will keep feeling awkward no matter how many times you do it. In this case, I think the most persuasive critique is that Dactal tries to keep the human language of queries in the vocabulary of the data, not the system, and the mechanics in punctuation, but "of" is uneasily poised somewhere between the two. You can work out what
topsong=(.of:@1.of#(.of.track info.album:album_type=album),(.of.ts):@1.of.track info)
is saying, but it's work. A query language should help humans talk to each other about our goals, not just help humans talk to computers about accomplishing them. Is that second "@1" in the right place? If we want each artist's second song, do we change one of these @1s to @2, or both, or something else? It's hard to tell. Actually, it's impossible to tell from looking at just this part of the query. You have to trace the logic back through the context of the rest of the query (or the data) to figure out where each "of" leaves you. Which also means that changes to the earlier parts of the query are likely to require changing this part, and in ways that also aren't obvious. Past-me knew what each "of" was doing when he wrote this; future-me is already getting prepared to resent past-me for making him rededuce that stuff again later.
2. Use the tools you already have. Dactal already has a way to create additional properties. So if we want to group tracks by artist and then be able to get back to the grouped tracks with "tracks" instead of saying "of", we can just do this:
tracks/artist|tracks=of
and now each group has both "tracks" and "of". This doubles the amount of data, though, and in multi-level logic that can quickly start to become a non-trivial cost.
3. If we're going to explore adding a new feature to grouping to handling this idea directly, we could just move "tracks=of" from a separate annotation (|) operation into the grouping operation:
tracks/artist,tracks=of
but that syntax already has a meaning, which is to group tracks by both artist and "tracks", where "tracks" is calculated by traversing the "of" property of the tracks. Tracks, in this dummy example, don't have an "of" property, but in the actual playlist query we started with, two of the three grouping layers are grouping previous groups, which do have "of"s, which is exactly the thing I'm trying to improve. So that's clearly not the way.
4. Doing the relabeling with the same syntax in the other order, however, like:
tracks/artist,of=tracks
sacrifices strict parallelism but actually fits into the existing model kind of nicely. Because groups have automatic "of" properties, it would already be problematic to use "of" as a grouping key. So this way fits a useful function into a previously unused space in the language. We haven't completely eliminated the system-vocabulary presence of "of", but now each "of" appears only once, in the bookkeeping of creating groups, and all subsequent logic about those groups can stick to the vocabulary of the data. So my original example becomes:topsong=(
.song:@1.songdates
#(.streams.track info.album:album_type=album),
(.streams.ts)
:@1.streams:@1.track info
)
and now not only is it clear exactly what each @1 means (the first is the first song, the second is the first of the re-sorted songdates), but it's easy to notice that we probably want that third @1 to pick the first song's first songdate's first stream, and given that we're sorting songdates entirely by properties from streams, maybe what we should really be doing is actually.song:@1.songdates
#(.streams.track info.album:album_type=album),
(.streams.ts)
:@1.streams:@1.track info
)
topsong=(.songs:@1.songdates.streams#(.track info.album:album_type=album),ts:@1.track info)
and now the query language is doing its real job of helping us think about what we intend to ask.
5. I implemented #4, but I do keep coming back to #2 in my mind. It might be generally useful to have a way of renaming existing properties instead of just duplicating them. Or a way of deleting them, for that matter. So I also implemented
tracks/artist|tracks=-of
for renaming, andtracks/artist|-of
for deleting. This pushes on issues of mutability and persistence that I probably haven't entirely thought through, so it might not be the right design, but trying is a way of finding out.The thing about "background music" is that you don't need special music in order to pay different attention to it. Or maybe you do, but you don't have to need it. The things you love, intently, can be your background. You just have to internalize that love, so that it feels like an integral part of you with which you move and live, not a novel surprise you are colliding with every time it happens. Even an artwork whose meaning cuts opens your heart is also just a surface of colors, or a timespan of sounds. Put your favorite painting on the wall and put a chair under it. Put your favorite songs on and just turn the volume down a little.
There wouldn't be a corrupt economy of aural jello-shot arbitrage if we all insisted on all our art being real.
There wouldn't be a corrupt economy of aural jello-shot arbitrage if we all insisted on all our art being real.
¶ P.S. (and all the other letters) · 9 January 2025 listen/tech
Software ought to be playful. Life ought to be playful, and thus we should want the tools we use to live it to allow or ideally encourage us to play, to improvise and experiment and digress as much as their seriousness allows. For airplane controls or heart-surgery robots the amount of allowable playfulness is probably low, but for most of the things we deal with in software, the software's ability to do arbitrarily frivolous things with an ease proportionate to inconsequentiality is a pretty good gauge of their expressiveness.
Say, for example, you wanted to produce a list of songs you liked last year, but just one song that begins with each letter of the alphabet. "Why?", someone might ask, but I suggest that "how?" is a more interesting question.
Here's how in Curio. Read and do this stuff if you haven't already, then go to the History page, pick playlist, scroll down to the bottom and click "see the query for this". This gives you the query that produces the playlist view, which is like taking apart your toaster to find the part that goes "ding", except that you can still use the toaster normally even though you've also taken it apart.
We're going to change just two things about this query: take out the part that limits it to 100 tracks, and then group the full list of potential tracks by first letter and pick the top track for each letter-group. Here's that playlist query, in red, with the one bit we need to remove crossed out, and the line we need to add in orange.
The new line groups the songs by "letter", which it defines by taking the name of the top song and splitting it into individual characters. The split function is usually used to break up lists at commas, that sort of useful thing, but if we frivolously split on nothing, which translates as ([]) in Dactal, we get a list of individual characters. The :@1 filters this list to just the first letter in it. Then .(.of:@1) says to take each letter group and go to its first track.
Here's what this gives me from my data:
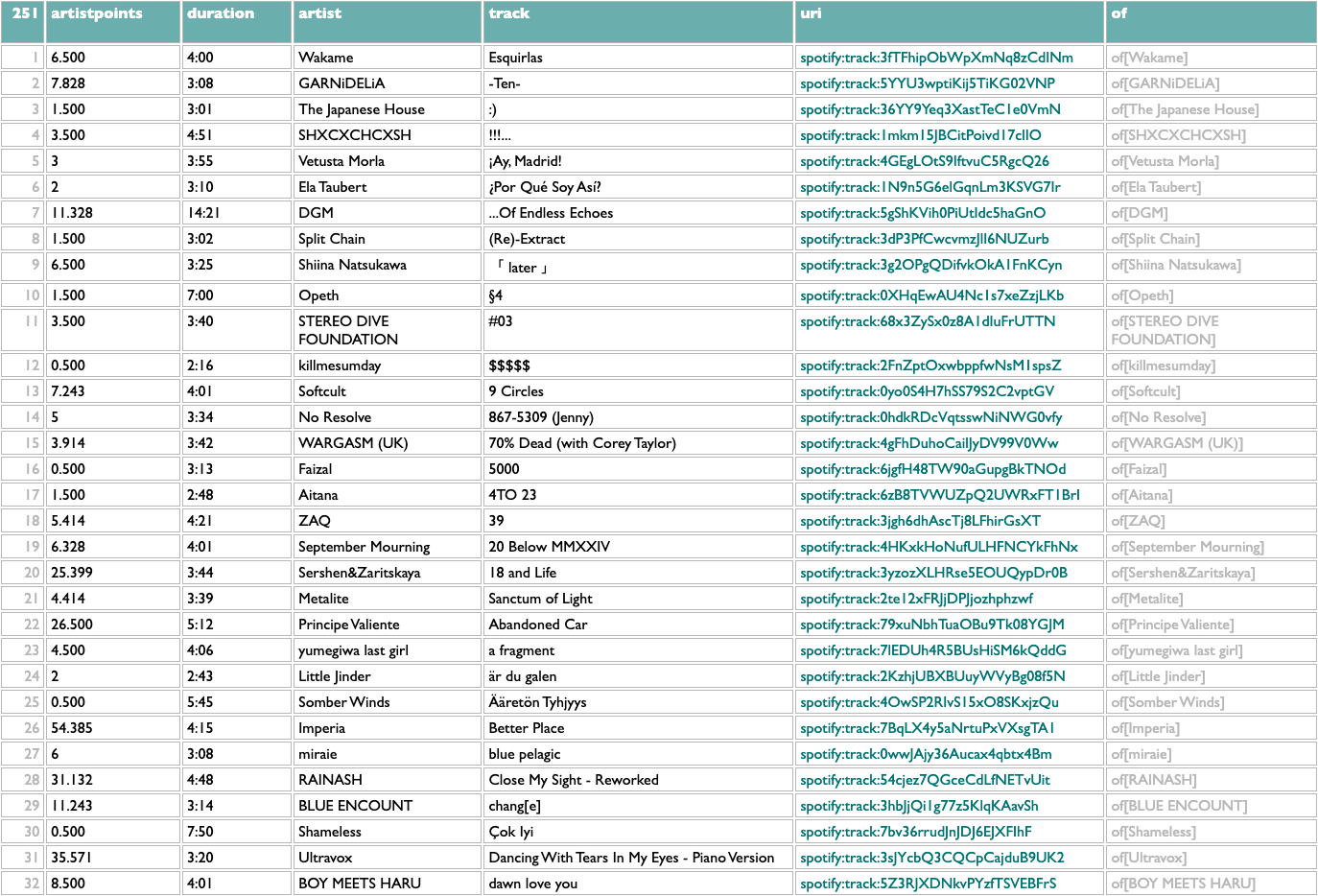
open this weird playlist in Spotify if you want; the premise is non-musical, but the music is still music...
Part of the point of making it easy to experiment is that you never really know what even the seemingly frivolous experiments are going to teach you. We might have thought we were going to get a list of 26 songs out of this, or if we had thought slightly harder we might have realized that we didn't take any steps to avoid songs that begin with punctuation marks, but there are several other maybe-intriguing things we can see here:
- uppercase and lowercase letters are different, obviously, and since song titles are not formally governed by the Chicago Manual of Style Convention, they can have any combination of cases
- accented characters like "Ç" are technically different letters, which will not be news to you if you know almost any language other than English, but maybe you don't
- there are a lot of languages in the world, and you probably do not listen to music in all of them, and neither do I, but still:
- so my obsessive fondness for Japanese kawaii metal and idol rock is most of how I got 251 letters instead of 26
But there are some other curious things here. What's going on with the first song, which seems to be called "Esquirlas", but is at the very top of the list instead of down in alphabetic order with the AaäÄBbCcÇ songs?
Let's find out. Curio is a web app, and the web is like a toolkit for building things that are easy to take apart. The adjustable screwdriver of web apps is the Inspect command. Right-click anything on a web page and pick Inspect.
Sometimes you will discover, if you do this, that the people who made the page did not expect you to, and the inside of their page is an incomprehensible mess of wires and crumbs and thus probably a fire hazard. But here's what the inside of this part of the Curio toaster looks like:
Ah! It looks like this song is called "Esquirlas" when you see it on the page, but in fact in the Spotify database it has a special character at the beginning which somehow comes out of the Spotify API as an (imaginary, I think) HTML entity. We may not think we care about this right now, but later when we're writing song-processing code and we don't understand why
What the hell is
We also learn one interesting thing about the typing I have done with my own weird fingers, because there are songs here beginning with most of the numbers. Not 6, though. There were no songs with titles beginning with the number 6 among my most-played single tracks by each artist. Is that right? We can cross-check.
Yes, apparently I did listen to "6km/h" by CHICKEN BLOW THE IDOL, and "666" by Ceres, but not as much as "rocket pencil" by CHIBLOW (as I assume we fondly refer to them) or "Humming" by Ceres. But the interesting thing I meant we see is that the numbers appear in this list in reverse order. That's my doing, because in my experience I mostly want numbers to be sorted from large to small, and in other query languages I found myself constantly having to sort by the negation of quantities to accomplish this, so I thought Dactal would be more expressive and improvisonational if the default was the other way around. But I didn't remember to handle it differently in the case where we're sorting names that begin with numbers. That's probably fixable. I'll work on fixing my toaster, that's my toaster oath.
What's yours?
[PPS from later:]

[PPPS: Hmm, also, what if we label the "of"s as we group, so that the back-references aren't so meta?]
Say, for example, you wanted to produce a list of songs you liked last year, but just one song that begins with each letter of the alphabet. "Why?", someone might ask, but I suggest that "how?" is a more interesting question.
Here's how in Curio. Read and do this stuff if you haven't already, then go to the History page, pick playlist, scroll down to the bottom and click "see the query for this". This gives you the query that produces the playlist view, which is like taking apart your toaster to find the part that goes "ding", except that you can still use the toaster normally even though you've also taken it apart.
We're going to change just two things about this query: take out the part that limits it to 100 tracks, and then group the full list of potential tracks by first letter and pick the top track for each letter-group. Here's that playlist query, in red, with the one bit we need to remove crossed out, and the line we need to add in orange.
2024 tracks full
/artist=(.track info.artists:@1),song=(.track info.name),date
|songdatepoints=(....count,sqrt)
/artist,song
||songpoints=(..of...songdatepoints,total),
songtime=(..of..of....ms_played,total)
#rank=songpoints,songtime
/artist
|artistpoints=(.of..songpoints..(...._,(0.5),difference)....total),
ms_played=(..of..songtime,total),
topsong=(.of:@1.of#(.of.track info.album:album_type=album),(.of.ts):@1.of.track info)
#artistpoints,ms_played:@<=100
/letter=(.topsong....name,([]),split:@1).(.of:@1)
.(...artistpoints=artistpoints,
duration=(.topsong....duration_ms,mmss),
artist=(.topsong.artists:@1.name),
track=(.topsong.name),
uri=(.topsong.uri))
/artist=(.track info.artists:@1),song=(.track info.name),date
|songdatepoints=(....count,sqrt)
/artist,song
||songpoints=(..of...songdatepoints,total),
songtime=(..of..of....ms_played,total)
#rank=songpoints,songtime
/artist
|artistpoints=(.of..songpoints..(...._,(0.5),difference)....total),
ms_played=(..of..songtime,total),
topsong=(.of:@1.of#(.of.track info.album:album_type=album),(.of.ts):@1.of.track info)
#artistpoints,ms_played:@<=100
/letter=(.topsong....name,([]),split:@1).(.of:@1)
.(...artistpoints=artistpoints,
duration=(.topsong....duration_ms,mmss),
artist=(.topsong.artists:@1.name),
track=(.topsong.name),
uri=(.topsong.uri))
The new line groups the songs by "letter", which it defines by taking the name of the top song and splitting it into individual characters. The split function is usually used to break up lists at commas, that sort of useful thing, but if we frivolously split on nothing, which translates as ([]) in Dactal, we get a list of individual characters. The :@1 filters this list to just the first letter in it. Then .(.of:@1) says to take each letter group and go to its first track.
Here's what this gives me from my data:

open this weird playlist in Spotify if you want; the premise is non-musical, but the music is still music...
Part of the point of making it easy to experiment is that you never really know what even the seemingly frivolous experiments are going to teach you. We might have thought we were going to get a list of 26 songs out of this, or if we had thought slightly harder we might have realized that we didn't take any steps to avoid songs that begin with punctuation marks, but there are several other maybe-intriguing things we can see here:
- uppercase and lowercase letters are different, obviously, and since song titles are not formally governed by the Chicago Manual of Style Convention, they can have any combination of cases
- accented characters like "Ç" are technically different letters, which will not be news to you if you know almost any language other than English, but maybe you don't
- there are a lot of languages in the world, and you probably do not listen to music in all of them, and neither do I, but still:

- so my obsessive fondness for Japanese kawaii metal and idol rock is most of how I got 251 letters instead of 26
But there are some other curious things here. What's going on with the first song, which seems to be called "Esquirlas", but is at the very top of the list instead of down in alphabetic order with the AaäÄBbCcÇ songs?
Let's find out. Curio is a web app, and the web is like a toolkit for building things that are easy to take apart. The adjustable screwdriver of web apps is the Inspect command. Right-click anything on a web page and pick Inspect.

Sometimes you will discover, if you do this, that the people who made the page did not expect you to, and the inside of their page is an incomprehensible mess of wires and crumbs and thus probably a fire hazard. But here's what the inside of this part of the Curio toaster looks like:

Ah! It looks like this song is called "Esquirlas" when you see it on the page, but in fact in the Spotify database it has a special character at the beginning which somehow comes out of the Spotify API as an (imaginary, I think) HTML entity. We may not think we care about this right now, but later when we're writing song-processing code and we don't understand why
songtitle == searchtitle isn't working, suddenly we might think "ohhhh, wait". And you might be tempted to think "nah, that probably won't ever happen again", but in fact it happens again just 20 lines down the page.

What the hell is
? Apparently it is a zero-width non-breaking space from the Unicode group Arabic Presentation Forms-B. What is it doing in the title of a song by the Swedish melodic power metal band Metalite? Apparently we do not know. Welcome to the wonderful world of trying to do anything with music data, or indeed pretty much any data that ever originated in humans typing with their weird fingers, which is essentially all data.
We also learn one interesting thing about the typing I have done with my own weird fingers, because there are songs here beginning with most of the numbers. Not 6, though. There were no songs with titles beginning with the number 6 among my most-played single tracks by each artist. Is that right? We can cross-check.
2024 tracks full:master_metadata_track_name~<6
Yes, apparently I did listen to "6km/h" by CHICKEN BLOW THE IDOL, and "666" by Ceres, but not as much as "rocket pencil" by CHIBLOW (as I assume we fondly refer to them) or "Humming" by Ceres. But the interesting thing I meant we see is that the numbers appear in this list in reverse order. That's my doing, because in my experience I mostly want numbers to be sorted from large to small, and in other query languages I found myself constantly having to sort by the negation of quantities to accomplish this, so I thought Dactal would be more expressive and improvisonational if the default was the other way around. But I didn't remember to handle it differently in the case where we're sorting names that begin with numbers. That's probably fixable. I'll work on fixing my toaster, that's my toaster oath.
What's yours?
[PPS from later:]

[PPPS: Hmm, also, what if we label the "of"s as we group, so that the back-references aren't so meta?]
2024 tracks full
/artist=(.track info.artists:@1),song=(.track info.name),date,of=streams
|songdatepoints=(....count,sqrt)
/artist,song,of=songdates
||songpoints=(..songdates...songdatepoints,total),
songtime=(..songdates..streams....ms_played,total)
#rank=songpoints,songtime
/artist,of=songs
|artistpoints=(..songs..songpoints..(...._,(0.5),difference)....total),
ms_played=(..songs..songtime,total),
topsong=(.songs:@1.songdates
#(.streams.track info.album:album_type=album),(.streams.ts)
:@1.streams:@1.track info)
#artistpoints,ms_played:@<=100
.(...artistpoints=artistpoints,
duration=(.topsong....duration_ms,mmss),
artist=(.topsong.artists:@1.name),
track=(.topsong.name),
uri=(.topsong.uri))
/artist=(.track info.artists:@1),song=(.track info.name),date,of=streams
|songdatepoints=(....count,sqrt)
/artist,song,of=songdates
||songpoints=(..songdates...songdatepoints,total),
songtime=(..songdates..streams....ms_played,total)
#rank=songpoints,songtime
/artist,of=songs
|artistpoints=(..songs..songpoints..(...._,(0.5),difference)....total),
ms_played=(..songs..songtime,total),
topsong=(.songs:@1.songdates
#(.streams.track info.album:album_type=album),(.streams.ts)
:@1.streams:@1.track info)
#artistpoints,ms_played:@<=100
.(...artistpoints=artistpoints,
duration=(.topsong....duration_ms,mmss),
artist=(.topsong.artists:@1.name),
track=(.topsong.name),
uri=(.topsong.uri))
¶ You choose the mood you seek · 8 January 2025 essay/tech
As an editor at a large publisher who liked my proposal for a book but was not going to publish it very reasonably explained to me, commercial publishers are in the business of publishing books that people already know they want to read. In books about music, as other editors told me less apologetically, this mostly means biographies of popular musicians. But glamour does generously leave a little shelf-space for fear, and so the book that a bigger publisher than mine thinks people already want to read is Liz Pelly's Mood Machine: The Rise of Spotify and the Costs of the Perfect Playlist. If you are the people they have in mind, who already wanted to read soberly-researched explanations of some of the ways in which a culture-themed capitalist corporation has pursued capitalism with a disregard for culture, written in a tone of muted resignation, here is your mood. For maximum irony, get the audiobook version and listen to it in the background while you organize your Pinterest boards of Temu products by Pantone color.
As a corporation, Spotify is very normal. Its Swedish origins render it slightly progressive in employment policies relative to American companies, at least if you want to have more children than you already have when you get hired, and can make sure to have them without getting laid off first. In business and product practices, I never saw much reason to consider it better or worse than what one would expect of a medium-to-large-sized publicly-traded tech company.
I arrived at Spotify involuntarily via an acquisition, and left involuntarily via a layoff, but in between those two events I was there voluntarily for a decade. I believe that music is what humans do best, and that bringing all(ish) of the world's music together online is one of the great human cultural achievements of my lifetime, and that the joy-amplifying potential of having the collective love and knowledge encoded in music-listening collated and given back to us is monumental. That's what I spent that decade working on, and although Spotify as a corporation finally voted decisively against this by laying me off and devoting considerable remaining resources to laboriously shutting down everything I worked on, I was hardly the only person working there who believed in music, and wanted there to be a music company that put music above "company", and wanted Spotify to behave in at least a few ways like that company.
It was never very likely to, of course. As Liz begrudgingly notes in her introduction, she set out to write an anti-Spotify book only to realize the problem wasn't really just Spotify so much as power. Spotify entered a music business largely controlled by a few record companies, at a point in history when the other confounding factors in the industry were already technological. Spotify did eventually come up with a few minorly novel forms of moral transgression, but they were never really in a position to explode the existing power structures, even if we could pretend they wanted to.
There were three specific things I fought against throughout my time at Spotify, and although my layoff was officially just part of a large impersonal reduction in "headcount", it's hard to imagine that there wasn't some connection. Mood Machine describes two of these in depressing detail: the secret preferential treatment of particular lower-royalty background music, and the not-secret "marketing" program to pressure artists to voluntarily accept lower royalty rates for the prospect of undisclosed algorithmic promotiom. Liz quotes multiple internal Spotify Slack messages about both these programs, and if somehow this ends up with all those grim private threads getting published, I'll be pleased to get so much of my earnest polemic-writing back. The quote from "yet another employee in the ethics-club" on pages 193-4, pointing out that Discovery Mode is exactly structured to benefit Spotify at the collective expense of artists, is definitely me. I'm pretty sure I went on to explain how to fix the economics of this by making Spotify's benefit conditional on artist benefit, and how to fix the morality of it by actually giving artists interesting agency instead of just an opportunity for submission. Sadly, Liz doesn't quote that part.
But I hadn't resigned in protest over PFC or Discovery Mode, partly because I didn't think either one actually caused sufficient practical damage that removing them would solve enough, but mostly because I had the autonomy and ability to spend my time fighting against the third and much bigger thing, which Mood Machine alludes to in far less detail than the others, which is Spotify's relentless and deliberate subordination of music and culture and humanity to machine learning. "ML Is the Product", the executive exhortation went. I wrote an internal talk explaining exactly why this was a culture-destructive way to think, which I would also like back. I am enthusiastically not against the use of data and algorithms in music and thus culture, but computers are tools that accomplish our human intents, and it is thus us that should be judged on their effects. Over the years at Spotify I found that it was increasingly dishearteningly common that people, and especially hierarchical company priorities based on obtuse quantitative metrics, not only did not care about the widely varying effects of erratic ML on music, but didn't even notice that they often didn't have enough information with which to care. I developed a small library of internal tools that only existed to make it unignorably easy to compare the outputs of two different systems on any individual example, and every time I ever compared a complicated state-of-the-art ML system developed by demonstrably talented ML engineers against whatever I whipped up in BiqQuery and spent a couple of hours tweaking while looking at exactly what it did for different bands or genres or songs, the music results from the less-exciting tech were always clearly better.
And each time I did this, it renewed my uncooperative senses of possibility and optimism, because collective human knowledge is astonishingly broad and deep, and the world is full of amazingly great music, and it takes only a little bit of very simple math to use the former to discover the latter. This is what my decade at Spotify was about, and thus is also what my book is about. If you care about music, you ought to want to read Liz's book. But if you can also stand being reminded why anybody cares about this subject in the first place, whether you already thought you wanted that or not, read mine, too.
Should you read either of our books? No. Do it if you want, or read something else, or put on some music and go for a walk, or put on some music and dance or hold still. My book is geeky, and tells you things you don't really have to know. Liz's is depressing, and tells you things you could already have guessed.
I will say, though, that mine involves both fears and joys. Liz's could have, but does not. It's telling that she talked to so many people, but as far as I can tell only people who she already knew agreed with her. Liz and I were on a Pop Conference panel together in 2018, I've offered to talk to her multiple times over the years, and she quotes my tweets and this blog and discusses my work in the book, but she didn't talk to me. Her book is decent journalism, but it's journalism to explicate a grudge, to deepen understanding in only one specific trench. I don't think, when you get to the bottom of it, there's any treasure, or really anything productive to do except climb back out, and then we're just where we started. Liz makes a good case for public libraries collecting local music, which seems like a fine idea to me, but not really an answer to any of the same questions. Mood Machine laments the loss of small things Liz thinks we used to have, maybe, but doesn't seem interested in looking for any of the big things we could have had, and still might. If the problem is mood, I don't think this is the solution.
Not that I solved anything in my book, either. We both note that maybe Universal Basic Income is really the only thing likely to. But if you think the only moral direction is retreat, and the right model for music is that you never hear any unless it was made next door, then you are choosing passivity over curiosity, and just a different status quo over all the possible better worlds, and reducing a complicated problem to choosing sides. And to me that's what we should be against, together.
As a corporation, Spotify is very normal. Its Swedish origins render it slightly progressive in employment policies relative to American companies, at least if you want to have more children than you already have when you get hired, and can make sure to have them without getting laid off first. In business and product practices, I never saw much reason to consider it better or worse than what one would expect of a medium-to-large-sized publicly-traded tech company.
I arrived at Spotify involuntarily via an acquisition, and left involuntarily via a layoff, but in between those two events I was there voluntarily for a decade. I believe that music is what humans do best, and that bringing all(ish) of the world's music together online is one of the great human cultural achievements of my lifetime, and that the joy-amplifying potential of having the collective love and knowledge encoded in music-listening collated and given back to us is monumental. That's what I spent that decade working on, and although Spotify as a corporation finally voted decisively against this by laying me off and devoting considerable remaining resources to laboriously shutting down everything I worked on, I was hardly the only person working there who believed in music, and wanted there to be a music company that put music above "company", and wanted Spotify to behave in at least a few ways like that company.
It was never very likely to, of course. As Liz begrudgingly notes in her introduction, she set out to write an anti-Spotify book only to realize the problem wasn't really just Spotify so much as power. Spotify entered a music business largely controlled by a few record companies, at a point in history when the other confounding factors in the industry were already technological. Spotify did eventually come up with a few minorly novel forms of moral transgression, but they were never really in a position to explode the existing power structures, even if we could pretend they wanted to.
There were three specific things I fought against throughout my time at Spotify, and although my layoff was officially just part of a large impersonal reduction in "headcount", it's hard to imagine that there wasn't some connection. Mood Machine describes two of these in depressing detail: the secret preferential treatment of particular lower-royalty background music, and the not-secret "marketing" program to pressure artists to voluntarily accept lower royalty rates for the prospect of undisclosed algorithmic promotiom. Liz quotes multiple internal Spotify Slack messages about both these programs, and if somehow this ends up with all those grim private threads getting published, I'll be pleased to get so much of my earnest polemic-writing back. The quote from "yet another employee in the ethics-club" on pages 193-4, pointing out that Discovery Mode is exactly structured to benefit Spotify at the collective expense of artists, is definitely me. I'm pretty sure I went on to explain how to fix the economics of this by making Spotify's benefit conditional on artist benefit, and how to fix the morality of it by actually giving artists interesting agency instead of just an opportunity for submission. Sadly, Liz doesn't quote that part.
But I hadn't resigned in protest over PFC or Discovery Mode, partly because I didn't think either one actually caused sufficient practical damage that removing them would solve enough, but mostly because I had the autonomy and ability to spend my time fighting against the third and much bigger thing, which Mood Machine alludes to in far less detail than the others, which is Spotify's relentless and deliberate subordination of music and culture and humanity to machine learning. "ML Is the Product", the executive exhortation went. I wrote an internal talk explaining exactly why this was a culture-destructive way to think, which I would also like back. I am enthusiastically not against the use of data and algorithms in music and thus culture, but computers are tools that accomplish our human intents, and it is thus us that should be judged on their effects. Over the years at Spotify I found that it was increasingly dishearteningly common that people, and especially hierarchical company priorities based on obtuse quantitative metrics, not only did not care about the widely varying effects of erratic ML on music, but didn't even notice that they often didn't have enough information with which to care. I developed a small library of internal tools that only existed to make it unignorably easy to compare the outputs of two different systems on any individual example, and every time I ever compared a complicated state-of-the-art ML system developed by demonstrably talented ML engineers against whatever I whipped up in BiqQuery and spent a couple of hours tweaking while looking at exactly what it did for different bands or genres or songs, the music results from the less-exciting tech were always clearly better.
And each time I did this, it renewed my uncooperative senses of possibility and optimism, because collective human knowledge is astonishingly broad and deep, and the world is full of amazingly great music, and it takes only a little bit of very simple math to use the former to discover the latter. This is what my decade at Spotify was about, and thus is also what my book is about. If you care about music, you ought to want to read Liz's book. But if you can also stand being reminded why anybody cares about this subject in the first place, whether you already thought you wanted that or not, read mine, too.
Should you read either of our books? No. Do it if you want, or read something else, or put on some music and go for a walk, or put on some music and dance or hold still. My book is geeky, and tells you things you don't really have to know. Liz's is depressing, and tells you things you could already have guessed.
I will say, though, that mine involves both fears and joys. Liz's could have, but does not. It's telling that she talked to so many people, but as far as I can tell only people who she already knew agreed with her. Liz and I were on a Pop Conference panel together in 2018, I've offered to talk to her multiple times over the years, and she quotes my tweets and this blog and discusses my work in the book, but she didn't talk to me. Her book is decent journalism, but it's journalism to explicate a grudge, to deepen understanding in only one specific trench. I don't think, when you get to the bottom of it, there's any treasure, or really anything productive to do except climb back out, and then we're just where we started. Liz makes a good case for public libraries collecting local music, which seems like a fine idea to me, but not really an answer to any of the same questions. Mood Machine laments the loss of small things Liz thinks we used to have, maybe, but doesn't seem interested in looking for any of the big things we could have had, and still might. If the problem is mood, I don't think this is the solution.
Not that I solved anything in my book, either. We both note that maybe Universal Basic Income is really the only thing likely to. But if you think the only moral direction is retreat, and the right model for music is that you never hear any unless it was made next door, then you are choosing passivity over curiosity, and just a different status quo over all the possible better worlds, and reducing a complicated problem to choosing sides. And to me that's what we should be against, together.
